 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
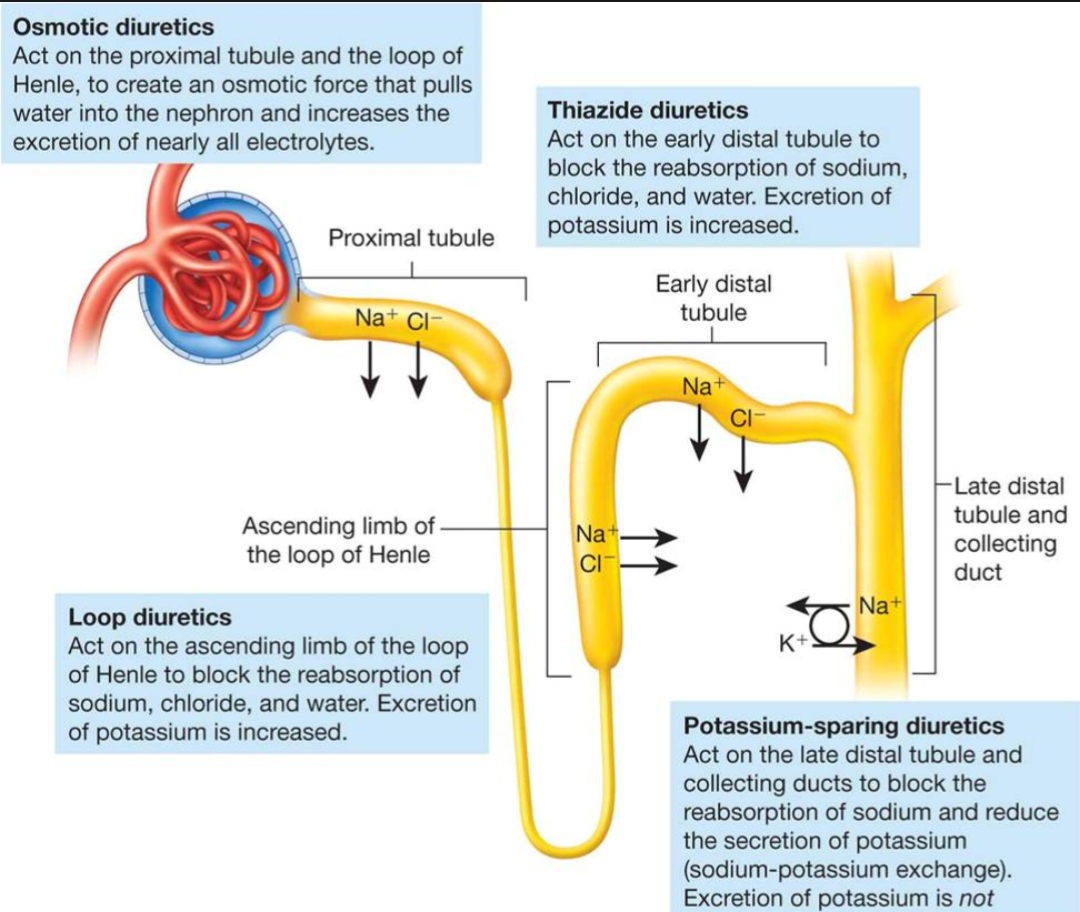
| Description: Osmotic diuretics Act on the proximal tubule and the loop of Henle, to create an osmotic force that pulls water into the nephron and increases the Thlazlde diuretics excretion of nearly all electrolytes. Act on the early distal tubule to block the reabsorption of sodium, chloride. and water. Excretion of potassium is increased. Early distal tubule Late distal Ascending limb of tubule and the loop of Henle collecting duct Loop diuretics Act on the ascending limb of the loop of Home to block the reabsorption of sodium, chloride. and water. Excretion of potassium is increased. Potassium-sparing diuretics Act on the late distal tubule and collecting ducts to block the reabsorption of sodium and reduce the secretion of potassium (sodium-potassium exchange). Excretion of potassium is not
Picture Stats: Views: 263 Filesize: 786.43kB Height: 912 Width: 1080 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=44440 |
