|
|
|
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.
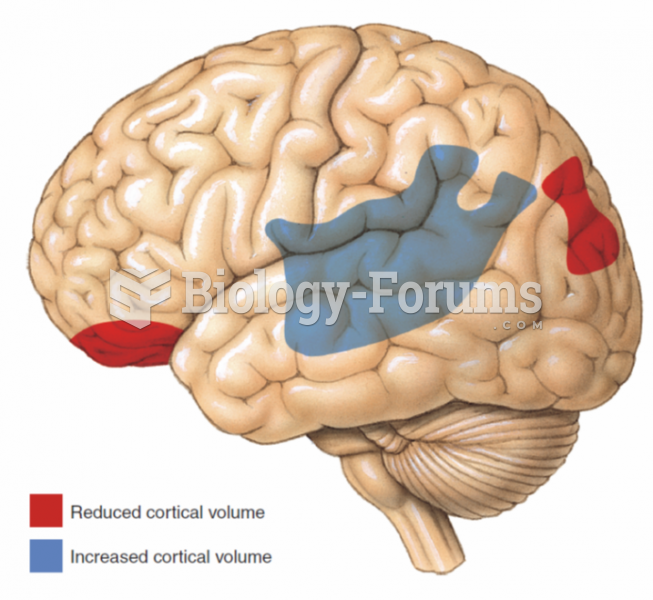
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.