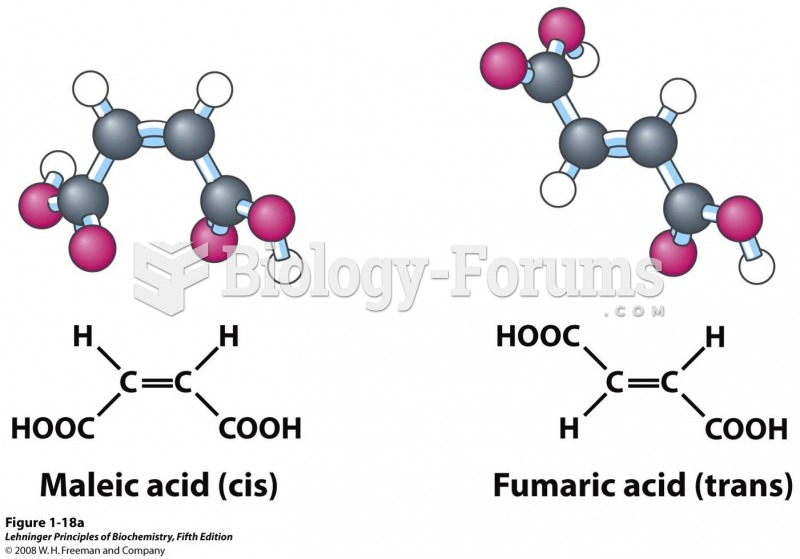
|
|
|
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
Atropine was named after the Greek goddess Atropos, the oldest and ugliest of the three sisters known as the Fates, who controlled the destiny of men.
Studies show that systolic blood pressure can be significantly lowered by taking statins. In fact, the higher the patient's baseline blood pressure, the greater the effect of statins on his or her blood pressure.