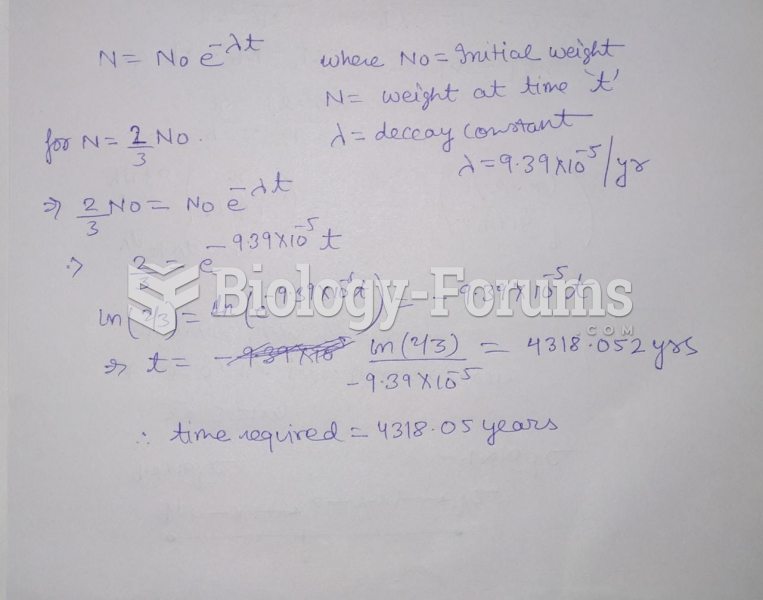
Answer to Question 1
Both nightmares and sleep terrors cause frightening experiences and hyperarousal for the individual experiencing them. Nightmares occur during REM sleep and usually awaken the sleeper. The nightmare is remembered by the individual and often makes the return to sleep difficult as a result. Sleep terror, in contrast, occur during stage 3 and stage 4 sleeps. The individual is hyperaroused and appears awake, but is unresponsive to external stimuli. Unlike the experience of a nightmare, sleep terrors are not remembered, and the return to sleep happens quickly after the event.
During REM sleep, motor output is inhibited so that voluntary movements are lost accompanied by a decrease in muscle tone. Sensory input from the external environment is also inhibited, but internal sensory awareness (particularly auditory and visual senses) is heightened. The autonomic nervous system causes fluctuations in blood pressure, heart rate, and respirations during REM sleep.
The function of REM is thought to involve the vivid dreaming that takes place during this stage. Central nervous system reprogramming is thought to occur during this stage, and previous experiences are processed in preparation for new ones to come. Learning experiences and memories are also processed and organized during this stage.
Good sleep hygiene involves creating an environment that ensures the best sleep possible. It involves practices such as going to bed at a regular time and sleeping long enough to feel refreshed. Appropriate sleep hygiene emphasizes the restriction of caffeinated products before sleeping and the elimination of distractions from the bedroom. Finally, good sleep hygiene addresses the external bedroom environment; the best sleep is achieved in a room that is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature.
Answer to Question 2
Dementia involves the deterioration of intellect to the extent that it interferes with occupational or social activity. Any disorder that damages the areas of the brain involved with memory and learning can result in dementia. Problem solving, memory, judgment, abstract thought, language, perception, and motor skills may all be affected in the presence of dementia.
Macroscopically, there is loss of neurons with cortical atrophy, particularly in the parietal and temporal lobes. The gyri narrow and the sulci deepen as tissue atrophies. The ventricles are also affected and enlarge as the brain mass declines.
Microscopically, neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles characterize Alzheimer disease. Neuritic plaques (or senile plaques) consist of degenerating nerve terminals that form clusters around a neurotoxic amyloid -peptide nucleus. The plaques are largely found in the neocortex, hippocampus, and isocortex. Neurofibrillary tangles develop in the cytoplasm of neurons. The tangles are composed of fibrous proteins and hyperphosphorylated tau proteins wrapped tightly in a helical fashion. They are resistant to enzymatic breakdown and compromise the function of the neuron they inhabit.
The hippocampus is central to the encoding and consolidation of short-term memory and retrieval of long-term memory. It is also responsible for the processing of information. In Alzheimer disease, the hippocampus is particularly vulnerable to the development of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. The production of choline acetyltransferase (an enzyme responsible for the synthesis of acetylcholine) declines as a result. When acetylcholine is deficient, the formation and processing of memory by the hippocampus are compromised.