 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
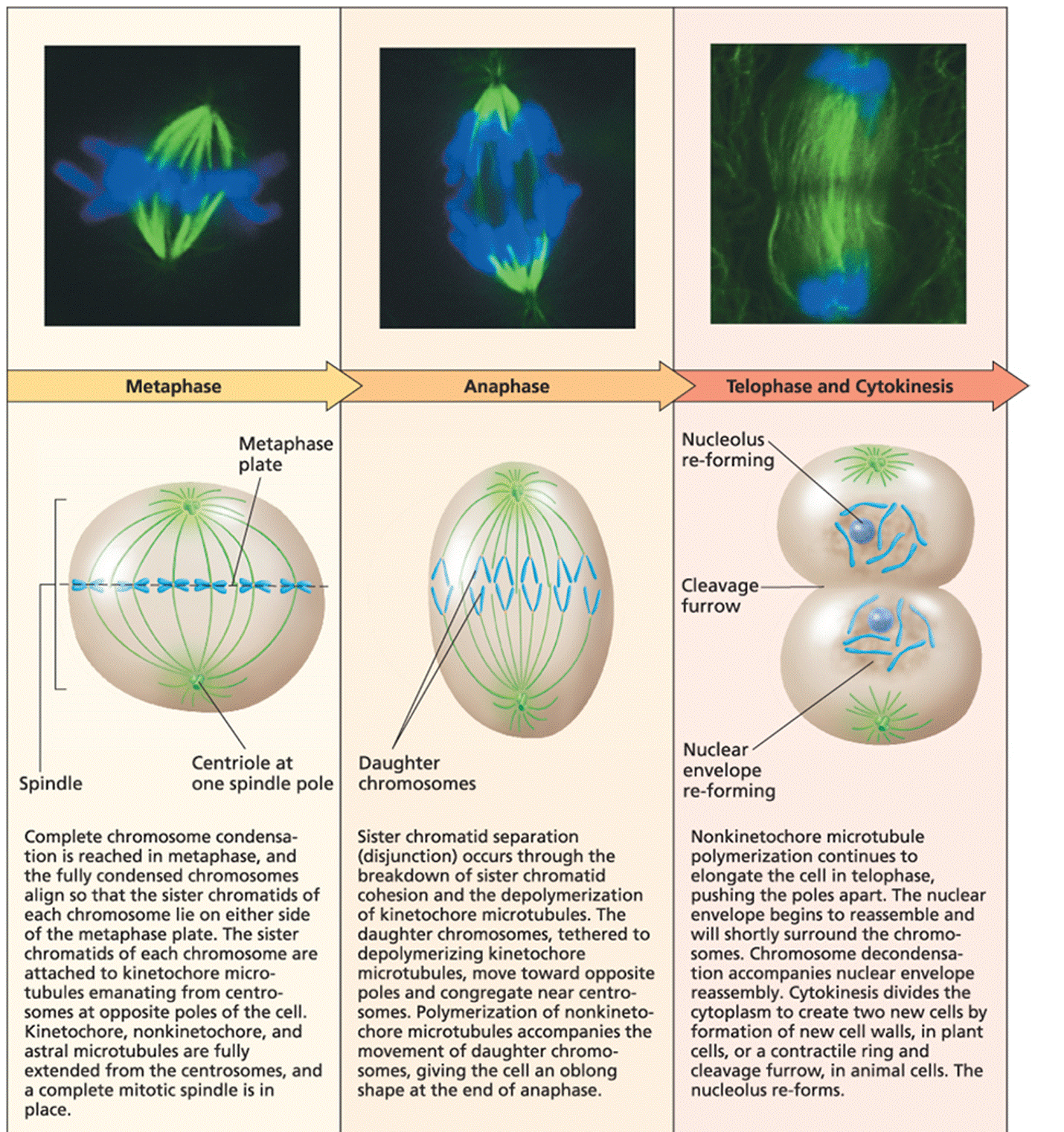
| Description: The chromosomes are shown in blue, and the centrosomes, asters, and spindle fibers are shown in green (2 of 2)The chromosomes are shown in blue, and the centrosomes, asters, and spindle fibers are shown in green (2 of 2) Metaphase r\\\ / Metaphase plate >3 . _..-- i \F- Centriole at one spindle pole Spindle Complete chromosome condensa- tion is reached in metaphase. and the fully condensed chromosomes align so that the sister chromatids of each chromosome lie on either side of the metaphase plate. The sister chromatids of each chromosome are attached to kinetochore micro- tubules emanating from centro- somes at opposite poles of the cell. Kinetochore, nonkinetochore, and astral microtubules are fully extended from the centrosomes. and a complete mitotic spindle is in place. Daughter chromosomes Sister chromatid separation (disjunction) occurs through the breakdown of sister chromatid cohesion and the depolymerization of kinetochore microtubules. The daughter chromosomes, tethered to depolymerizing kinetochore microtubules. move toward opposite poles and congregate near centro- somes. Polymerization of nonkineto« chore microtubules accompanies the movement of daughter chromo- somes, giving the cell an oblong shape at the end of anaphase. Nucleolus reforming Cleavage furrow Nuclear envelope re~forming Nonkinetochore microtubule polymerization continues to elongate the cell in telophase, pushing the poles apart. The nuclear envelope begins to reassemble and will shortly surround the chromo- somes. Chromosome decondensa- tion accompanies nuclear envelope reassembly. Cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm to create two new cells by formation of new cell walls, in plant cells, or a contractile ring and cleavage furrow, in animal cells. The nucleolus re-forms. Picture Stats: Views: 158 Filesize: 903.96kB Height: 1522 Width: 1430 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=48598 |
