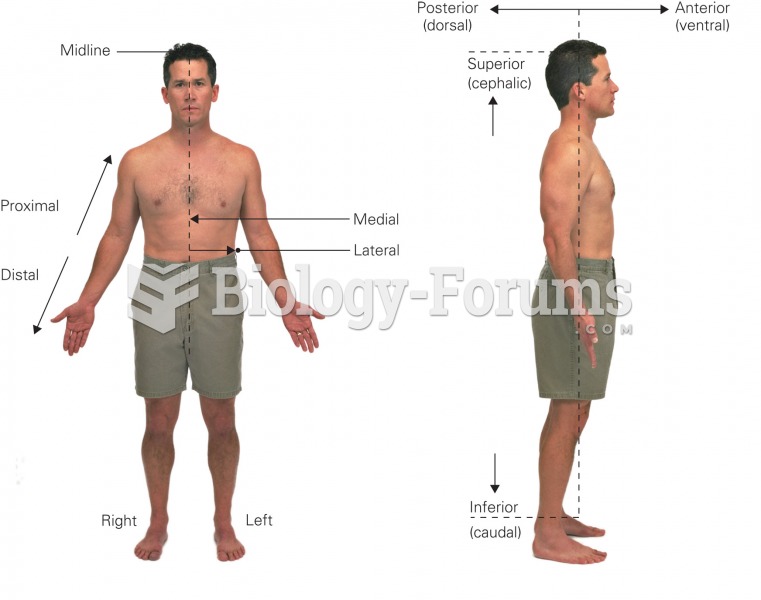
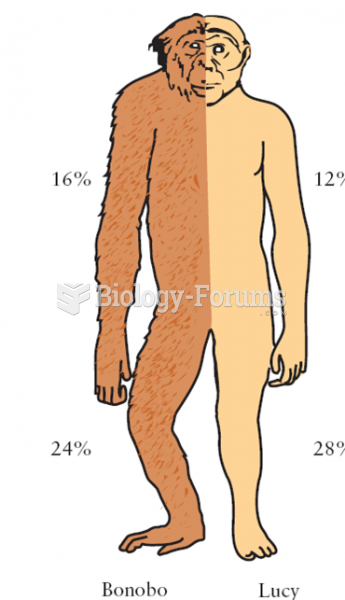
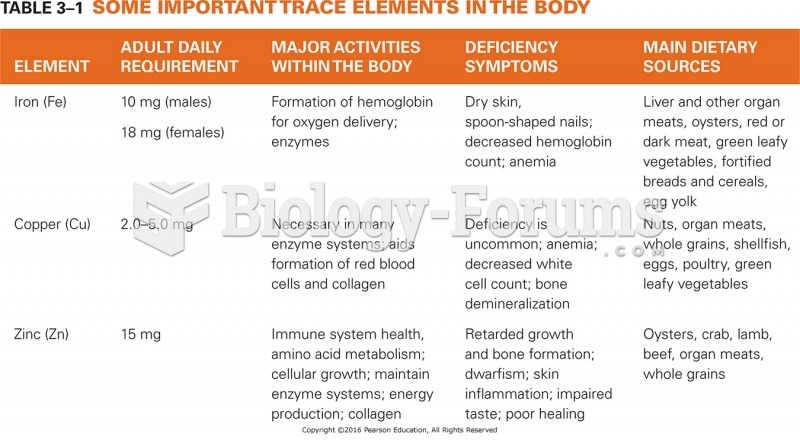
|
|
|
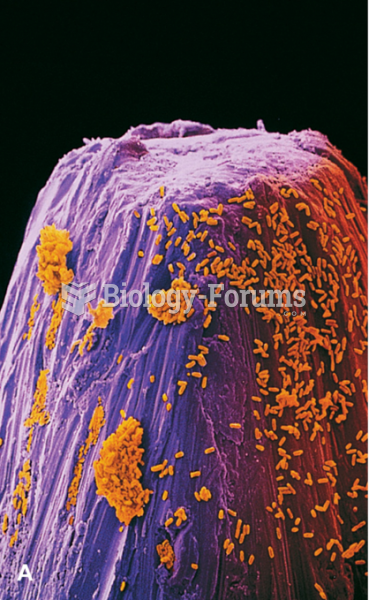
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
Asthma attacks and symptoms usually get started by specific triggers (such as viruses, allergies, gases, and air particles). You should talk to your doctor about these triggers and find ways to avoid or get rid of them.
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
A strange skin disease referred to as Morgellons has occurred in the southern United States and in California. Symptoms include slowly healing sores, joint pain, persistent fatigue, and a sensation of things crawling through the skin. Another symptom is strange-looking, threadlike extrusions coming out of the skin.