Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: The nurse can answer this question.
Rationale 2: This answer does not address the client's question and makes the nurse appear reluctant to answer.
Rationale 3: The various components of the immune system work together as a single unit to accomplish effective immune surveillance. A malfunction in any portion of the system may affect the effectiveness of the entire lymphatic system.
Rationale 4: Autoimmune diseases can be described as the body working against itself. This is not the same as ineffective immune surveillance.
Global Rationale: The components of the lymphatic system provide the body with immunity, which is the ability to resist injury and infections. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of cells, vessels, and tissues that provide immune surveillance. Although the lymphatic system can be divided into individual structures and components for ease of study, it is best to think of it as an integrated whole. The various components of this system are in continuous communication and work together as a single unit to accomplish effective immune surveillance. A malfunction in any one single component may affect the effectiveness of the entire lymphatic system. The nurse should be prepared to answer client questions such as this one and should not appear reluctant to do so. Autoimmune diseases can be described as the body working against itself. This is not the same as ineffective immune surveillance.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1
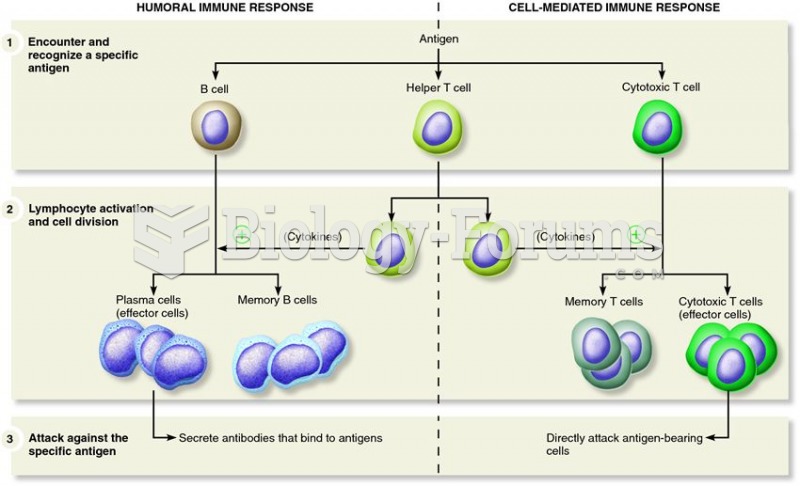
Rationale 1: Activation of the humoral immune system results in antibodies.
Rationale 2: Activation of the humoral immune system does not result in macrophages.
Rationale 3: Activation of the humoral immune system does not result in T lymphocytes.
Rationale 4: Activation of the humoral immune system does not result in NK cells.
Global Rationale: The humoral immune response is triggered when an antigen encounters a B lymphocyte, more simply known as a B cell. The activated B cell divides to form millions of identical copies of it-self in a process known as clonal division. Most cells in this clone are called plasma cells, whose primary function is to secrete antibodies specific to the antigen that initiated the challenge. The activation of complement, with subsequent inflammation and enhanced phagocytosis, is a major defense mechanism resulting from the formation of antigenantibody complexes. Peak production of antibodies occurs about 10 days after an initial antigen challenge. Activation of the humoral immune system does not result in macrophages, T lymphocytes, or NK cells.