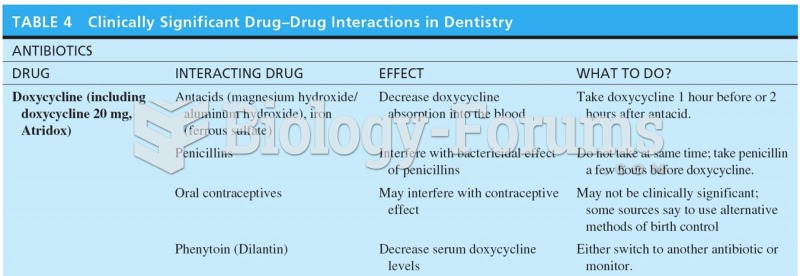
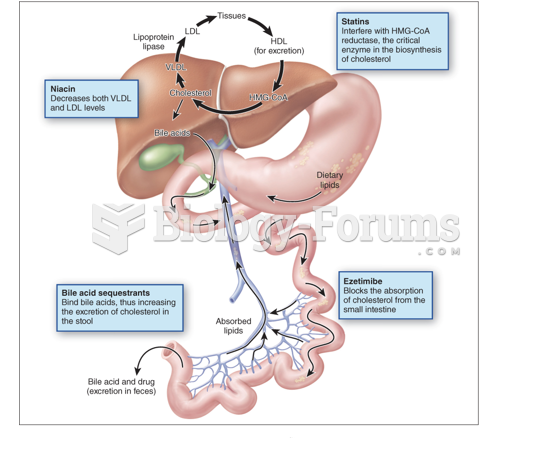
Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: In contrast to other methods of excretion, the lungs excrete most drugs in their original unmetabolized form, via exhalation.
Rationale 2: Defecation excretes most drugs in a metabolized form.
Rationale 3: Sweating excretes most drugs in a metabolized form.
Rationale 4: Urination excretes most drugs in a metabolized form.
Global Rationale: In contrast to other methods of excretion, the lungs excrete most drugs in their original unmetabolized form, via exhalation. Defecation, sweating, and urination excrete most drugs in a metabolized form.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Involves the kidneys is incorrect because enterohepatic recirculation involves the liver.
Rationale 2: Elimination of drugs through bile can continue for several weeks after therapy has stopped, and results in prolonged drug action.
Rationale 3: Results in decreased drug action is incorrect because recirculating drugs are then metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys. The fraction of drug that is not recirculated continues on its way to the feces. Elimination of drugs through bile can continue for several weeks after therapy has stopped, and results in prolonged drug action.
Rationale 4: Does not affect drug action is incorrect because recirculating drugs are then metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys. The fraction of drug that is not recirculated continues on its way to the feces. Elimination of drugs through bile can continue for several weeks after therapy has stopped, and results in prolonged drug action.
Global Rationale: Elimination of drugs through bile can continue for several weeks after therapy has stopped, and results in prolonged drug action. Involves the kidneys is incorrect because enterohepatic recirculation involves the liver. Results in decreased drug action is incorrect because recirculating drugs are then metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys. The fraction of drug that is not recirculated continues on its way to the feces. Elimination of drugs through bile can continue for several weeks after therapy has stopped, and results in prolonged drug action. Does not affect drug action is incorrect because recirculating drugs are then metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys. The fraction of drug that is not recirculated continues on its way to the feces. Elimination of drugs through bile can continue for several weeks after therapy has stopped, and results in prolonged drug action.