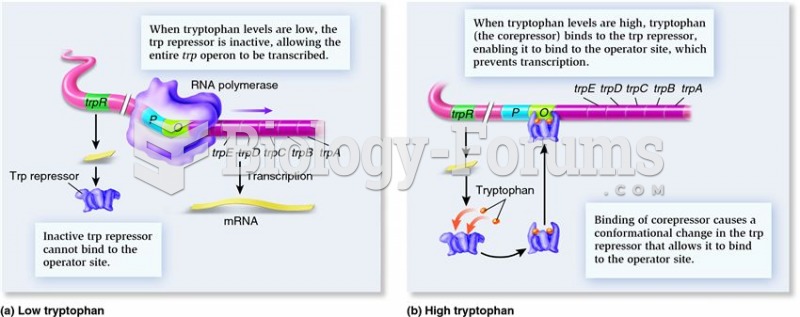
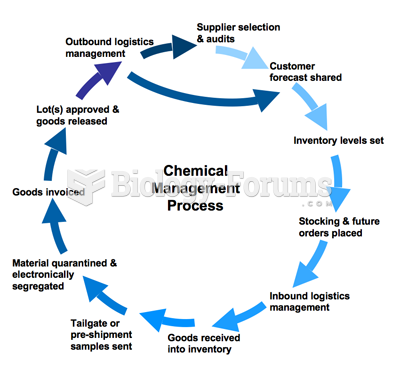
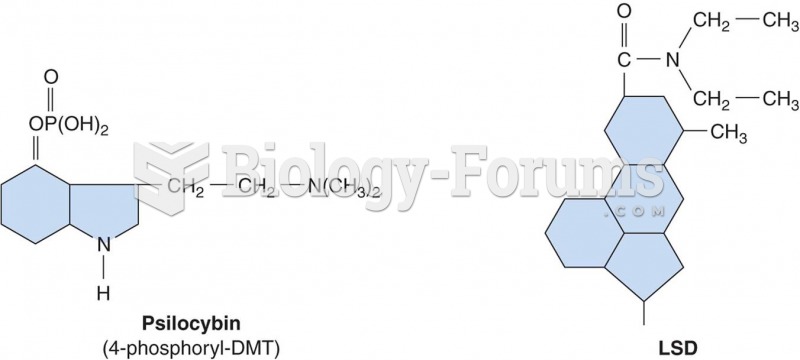
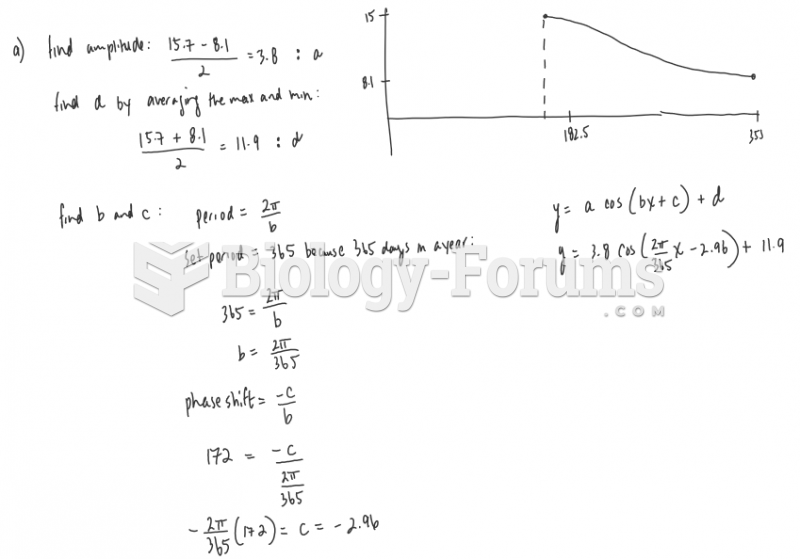
Answer to Question 1
ANS:
The use of pesticides has helped to generate higher crop yields that feed the world and protect against diseases transmitted by insects. Still, many consumers are leery. To feed a nation while using fewer pesticides requires creative farming methods. These methods include such practices as rotating crops, releasing organisms into fields to destroy pests, and planting non- food crops nearby to kill pests or attract them away from the food crops. For example, releasing sterile male fruit flies into orchards helps to curb the population growth of these pests; some flowers, such as marigolds, release natural insecticides and are often planted near crops such as tomatoes. Such alternative farming methods are more labor-intensive and may produce smaller yields than conventional methods, at least initially. Over time, though, by eliminating expensive pesticides, fertilizers, and fuels, these alternatives may actually cut costs more than they cut yields.
Answer to Question 2
ANS:
Consumers depend on the EPA and the FDA to keep pesticide use within safe limits. If the pesticide is approved, the EPA establishes a tolerance level for its presence in foods, well below the level at which it could cause any conceivable harm. Tolerance regulations also state the specific crops to which each pesticide can be applied. If a pesticide is misused, growers risk fines, lawsuits, and destruction of their crops.
Once tolerances are set, the FDA enforces them by monitoring foods and livestock feeds for the presence of pesticides. Over the past several decades of testing, the FDA has seldom found residues above tolerance levels, so it appears that pesticides are generally used according to regulations. Minimal pesticide use means lower costs for growers. In addition to costs, many farmers are also concerned about the environment, the quality of their farmland, and a safe food supply. Where violations are found, they are usually due to unusual weather conditions, use of unapproved pesticides, or misusefor example, application of a particular pesticide to a crop for which it has not been approved.
The FDA collects and analyzes samples of both domestic and imported foods. If the agency finds samples in violation of regulations, it can seize the products or order them destroyed. Individual states also scan for pesticides (as well as for industrial chemicals) and provide information to the FDA.
In addition to its ongoing surveillance, the FDA conducts focused sampling to determine the presence of particular pesticides in specific crops. For example, the agency might search for aldicarb in potatoes, captan in cherries, and diaminozide (the chemical name for Alar) in apples, among others.
In addition to monitoring crops in the field for pesticides, the FDA also monitors people's actual intakes. The agency conducts the Total Diet Study (sometimes called the Market Basket Survey) to estimate the dietary intakes of pesticide residues by eight age and gender groups from infants to senior citizens. Four times a year, FDA surveyors buy almost 300 foods from US grocery stores, each time in several cities. They prepare the foods table ready and then analyze them not only for pesticides, but also for essential minerals, industrial chemicals, heavy metals, and radioactive materials. In all, the survey reports on more than 6000 samples a year, including samples imported from 100 countries. Most heavily sampled are fresh vegetables, fruits, and dairy products.
A substantial and increasing amount of the fruits and vegetables consumed in the United States are imported from other countries. These countries have their own pesticide regulationssome more, and others less, stringent than those in the United States. To export into the United States, countries are required to comply with US pesticide tolerance limits, but FDA testing of imported produce is fairly limited. Consequently, the extent to which US consumers are exposed to elevated levels of pesticide residues from imported foods compared with domestic crops is relatively unknown.