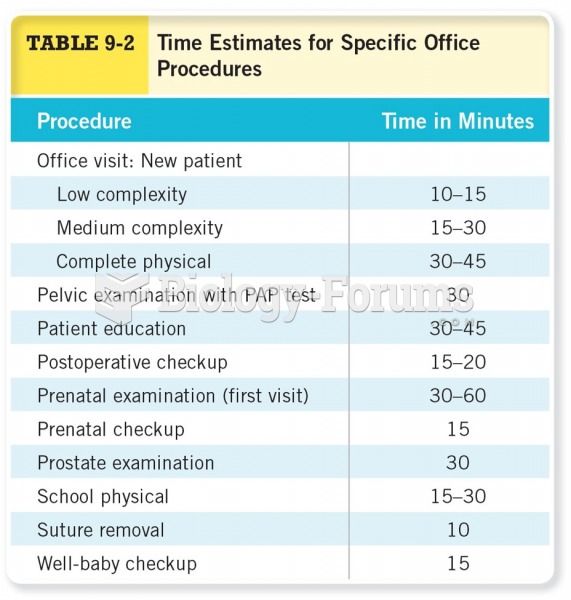
Answer to Question 1
There are several specific nutrients that should be considered when designing nutrition support for a trauma patient. These include glutamine, arginine, and omega-3 fatty acids, which all have an immune-enhancing effect for the metabolically stressed patient. Glutamine is typically the most abundant amino acid in the body that is utilized by immune competent cells, enterocytes, and hepatocytes, but glutamine becomes depleted in critically ill and surgical patients. Enteral glutamine supplementation may improve gut barrier function and lymphocyte function, however, recent reports indicate that parenteral glutamine should only be used with caution, as there are conflicting reports in the literature with respect to length of hospital stay, infections and survival. .
Arginine is the precursor to nitric oxide and becomes an essential amino acid during metabolic stress. During metabolic stress, it can be beneficial by playing a role in wound healing through several potential mechanisms, such as enhanced collagen and hydoxyproline formation. Also, it promotes normalization of T-cell function, which is important in order to blunt the inflammatory response. Arginine is converted in the body to nitric oxide, which increases blood vessel dilation for improved blood flow and stimulates the release of growth hormone, insulin, and other anabolic substances. Excess arginine could be harmful in patients who are hemodynamically unstable. Arginine should be used with caution in critically ill patients, especially those in the ebb phase of the metabolic stress response.
Omega-3 fatty acids aid the immune system by competing with omega-6 fatty acids (arachidonic acid) for cyclooxygenase metabolism at the cellular membrane. This allows for fewer inflammatory and immunosuppressive eicosanoids to be produced and thus reduces the inflammatory response. There is currently no standard dosage for omega-3 fatty acids, but typically up to 5 grams/day have been used in critically ill patients with sepsis. Caution should be exercised in those patients with coagulation disorders as an excess amount of omega 3 fatty acids can reduce platelet aggregation. Much more research needs to be conducted in order to make these recommendations more routine in the acute care setting
Answer to Question 2
IBS is a functional disorder, which means that other GI diseases that present with similar symptoms (celiac, Crohn's, infectious diarrhea, etc.) are ruled out before diagnosing the patient with irritable bowel syndrome.
A colonoscopy is an endoscopic exam of the colon, or the large intestine. This exam would see diverticulitis or polyps, which are pre-cancerous growths that may develop into colon cancer. Mrs. Clarke's colonoscopy was normal, indicating that diverticulosis, diverticulitis, and ulcerative colitis/Crohn's disease (inflammatory bowel diseases) are ruled out. In addition, the colonoscopy is a part of screening to rule out colon cancer.
The hydrogen breath test is used to detect lactose malabsorption or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Lactose malabsorption is often associated with IBS. Baseline hydrogen on the breath is measured. The patient then consumes 25-50 g of lactose and breath hydrogen concentration is measured after 3-8 hours. >20 ppm indicates lactose malabsorption. Depending on the outcome of the scheduled hydrogen breath test, positive results may aid in assistance with nutrition therapy.
Anti-tTG are antibodies associated with celiac disease (CD). The identification of antibodies is commonly used to diagnose CD. A negative result for these antibodies would rule out CD for Mrs. Clarke. Celiac disease is also associated with IBS so the American College of Gastroenterology recommends that all patients be screened for celiac disease as a component of differentiating the diagnosis from IBS.