|
|
|
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
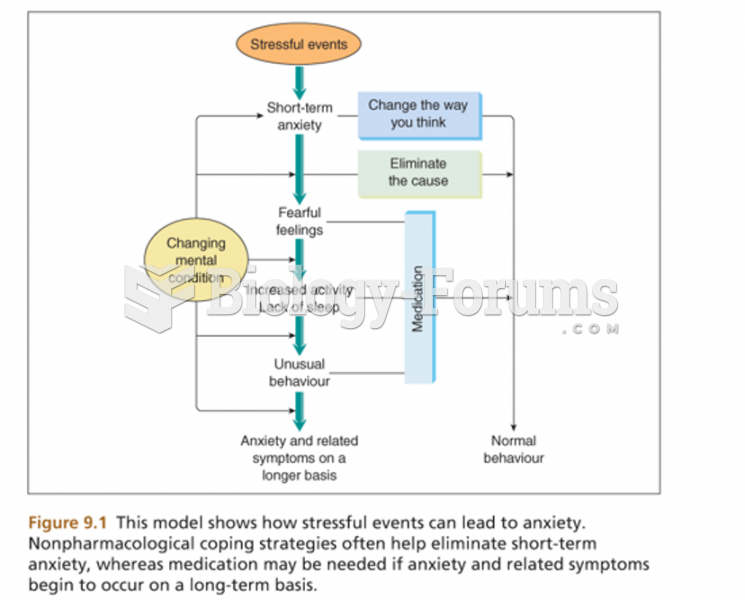
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
More than 20 million Americans cite use of marijuana within the past 30 days, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). More than 8 million admit to using it almost every day.