|
|
|
It is widely believed that giving a daily oral dose of aspirin to heart attack patients improves their chances of survival because the aspirin blocks the formation of new blood clots.
The most common childhood diseases include croup, chickenpox, ear infections, flu, pneumonia, ringworm, respiratory syncytial virus, scabies, head lice, and asthma.
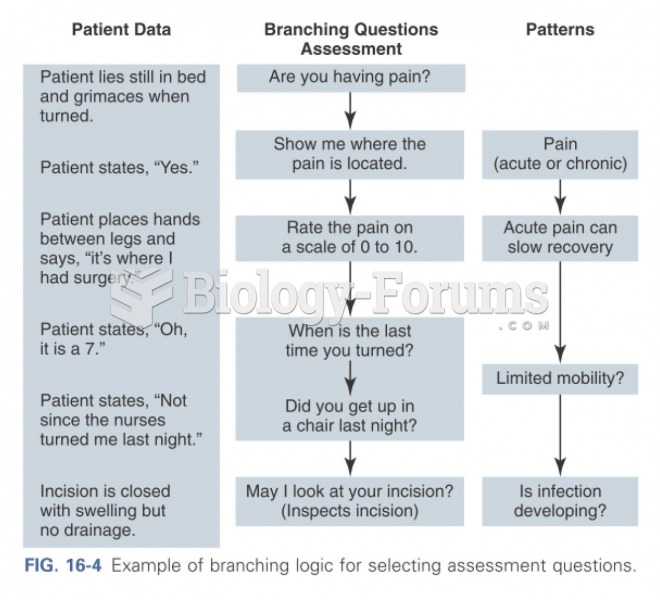
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).
People often find it difficult to accept the idea that bacteria can be beneficial and improve health. Lactic acid bacteria are good, and when eaten, these bacteria improve health and increase longevity. These bacteria included in foods such as yogurt.
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.