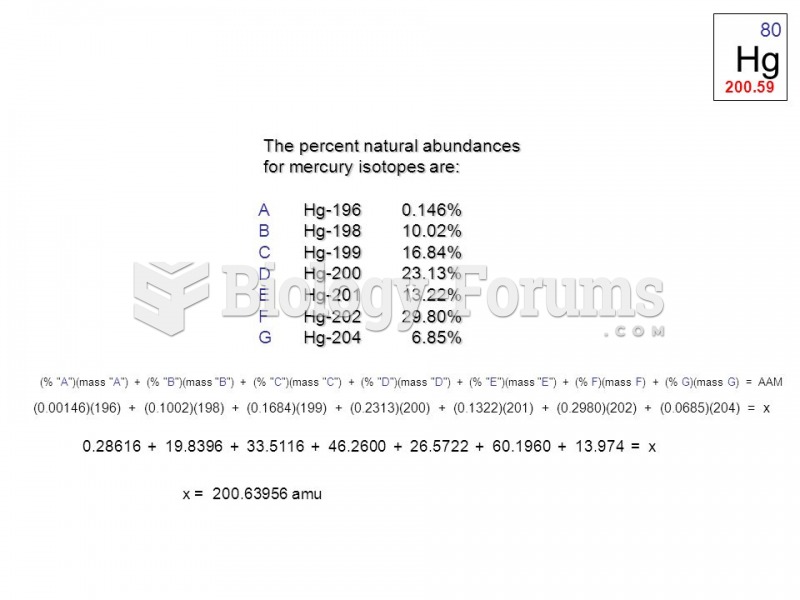
Answer to Question 1
ANSWER:
Mutations are errors that occur when DNA is replicated. The average human baby is born with about 130 new mutations, but the vast majority have no effect. Mutant alleles that provide some advantage often spread through the population, but most mutant alleles that result in a disadvantage disappear from future generations. Example: The original appearance of the allele for blonde hair was probably the result of a random mutation that occurred in Northern Europe some 10,000 years ago.
Migration occurs when organisms move from one geographical location to the next. Phenotypical traits that are advantageous in one environment might be less so in another. Example: Migration, or rather the lack of it, might account for the relatively restricted area in Northern Europe populated by blondes until fairly recent times. Geographical barriers of mountain and ocean contained the blonde allele for many centuries.
Genetic drift produces change from one generation to the next through chance or accident. Example: Genetic drift undoubtedly reduced the global frequency of the blonde allele between 1300 and 1700, as waves of Bubonic plague decimated the European population, which at that time contained nearly everyone carrying the blonde allele. If by chance every single person carrying the blonde allele had died from the plague before reproducing, the allele would have disappeared from the human genome.
Natural selection is the process by which survival and reproduction pressures act to change the frequency of alleles in subsequent generations. Example: The continuation of the blonde hair allele may have been influenced by natural selection. When a person has a choice of mates of equal value, he or she will select the one that stands out from the crowd. Individuals with blonde hair color, which was different and more rare, might have enjoyed more reproductive success than those with more common, darker hair colors.
Answer to Question 2
ANSWER:
Heritability is the statistical likelihood that variations observed across individuals in a population are due to genetics. Heritability is usually presented as a ratio of the amount of variation observed in a population due to genetics relative to the total amount of variation due to both genetic and environmental influences. Heritability is a concept that is frequently misunderstood. Heritability always refers to populations, not to individuals. Saying that a trait such as shyness is 40 heritable does not say that 40 of one individuals shyness is produced by genes and the other 60 by the environment. Instead, a 0.40 heritability ratio suggests that the variations in shyness we see across the population (from very high to very low) are influenced moderately by both genetic and environmental factors.
If genes play no part in producing phenotypical differences between individuals, heritability is zero. For example, genes are responsible for us having hearts, but there is no individual variation in the population in terms of the presence of a heartwe all have one. Consequently, the heritability of having a heart is 0.0. If genes are totally responsible for all phenotypical differences between individuals, heritability is 1.0. All variation in the population in terms of having or not having a fatal neurological condition known as Huntingtons disease is entirely due to genetics. If you inherit a Huntingtons gene from one parent, you will develop the condition, so the heritability of Huntingtons is 1.0.
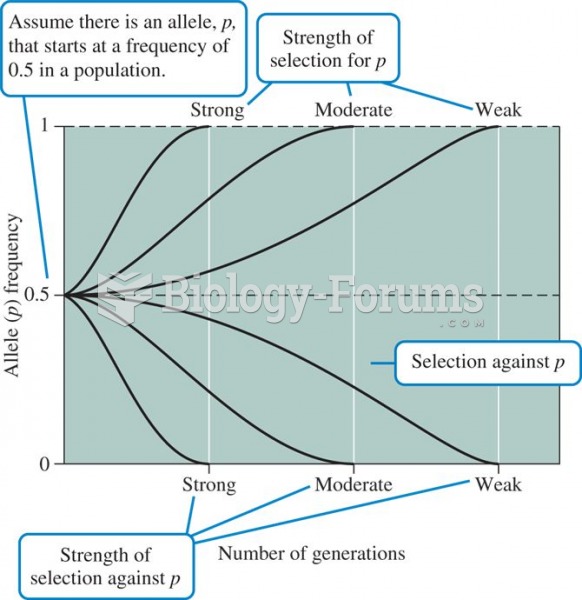 Variation in the rate of evolution as a function of the strength of selection, assuming genetic drif
Variation in the rate of evolution as a function of the strength of selection, assuming genetic drif
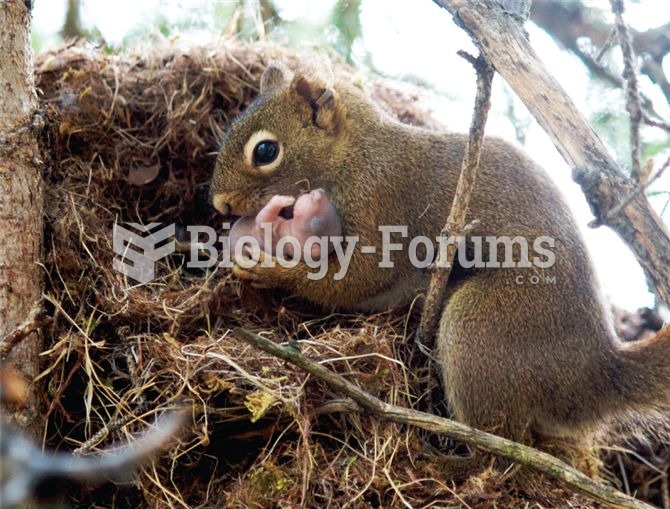 Some red squirrels adopt the offspring of related individuals, a likely example of kin selection pro
Some red squirrels adopt the offspring of related individuals, a likely example of kin selection pro