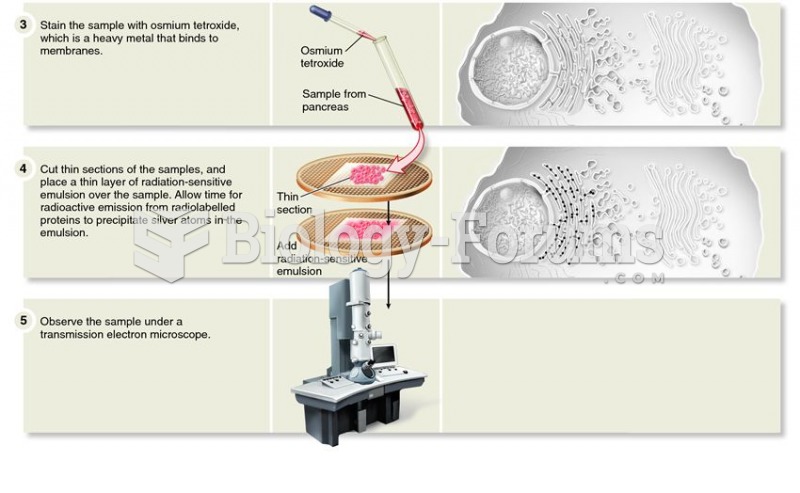
Answer to Question 1
ANS: B, D, F
Power is the probability that a statistical test will detect an effect when it actually exists. Therefore, power is the inverse of type II error and is calculated as 1 . Recall that type II error is the probability of retaining the null hypothesis when it is in fact false. When the researcher sets type II error at 0.20 prior to conducting a study, this means that the power of the planned statistic has been set to 0.80. In other words, the statistic will have an 80 chance of detecting an effect if it actually exists. Often, reported studies failing to reject the null hypothesis (in which power is unlikely to have been examined) will have a low power level to detect an effect if one exists. Until recently, the researcher's primary interest was in preventing a Type I error. Therefore, great emphasis was placed on the selection of a level of significance but little on power. This point of view is changing. Power analysis involves determining the required sample size needed to conduct the study. Cohen identified four parameters of power: (1) significance level, (2) sample size, (3) effect size, and (4) power. If three of the four are known, the fourth can be calculated by using power analysis formulas. Effect size is a constant; it is the degree to which the phenomenon is present in the population or the degree to which the null hypothesis is false. Consequently, if the researcher wants to increase a study's power, the sample size must be increased, or the level of significance must be set at a less stringent level.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: A, B, D, E
The following steps outline each of the components of statistical hypothesis testing. The null hypothesis is stated. The study alpha (type I error) is set. The study beta (type II error) is set. A power analysis is performed. The study is conducted. The statistic is computed, based on the data obtained. The obtained statistic is compared with the critical value for the alpha chosen. If the obtained statistic is greater than the critical value, the null hypothesis is rejected; if the obtained statistic is less than the critical value, the null hypothesis is accepted.
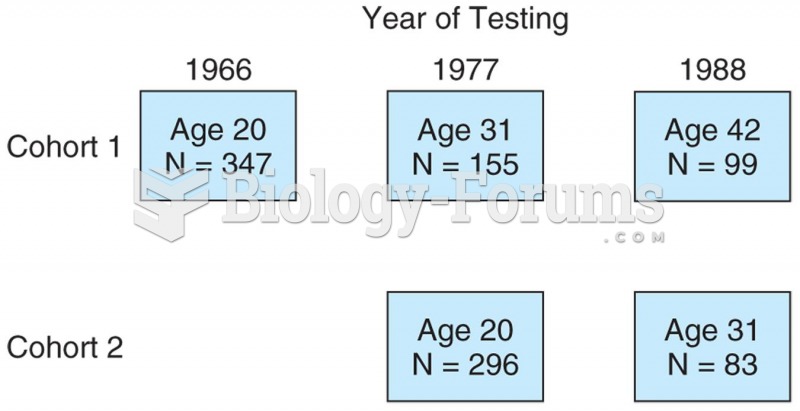 Model of a sequential study in which two cohorts were followed beginning at age 20. One cohort was f
Model of a sequential study in which two cohorts were followed beginning at age 20. One cohort was f
 If sociologists were to study land diving on Pentecost Island in Vanuatu, they could use a variety ...
If sociologists were to study land diving on Pentecost Island in Vanuatu, they could use a variety ...