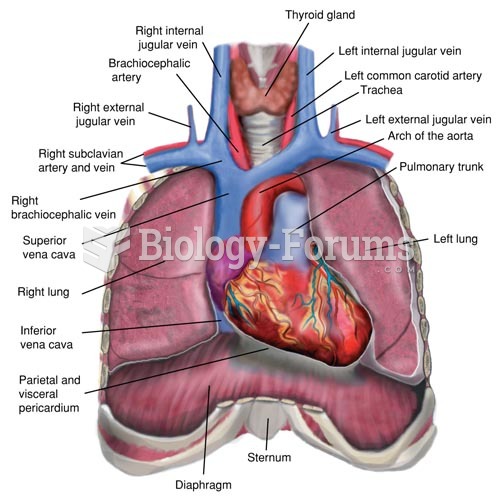
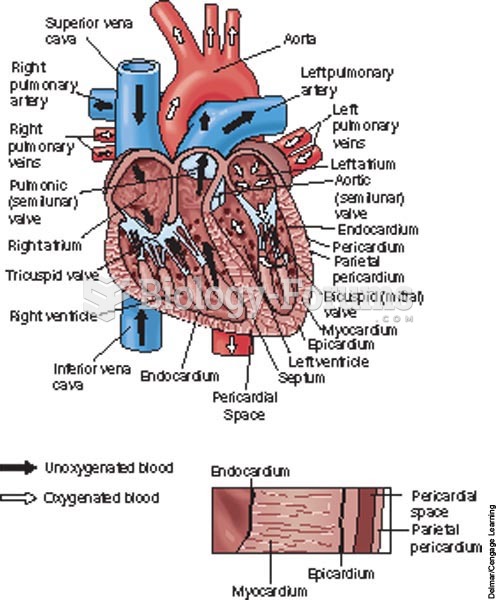
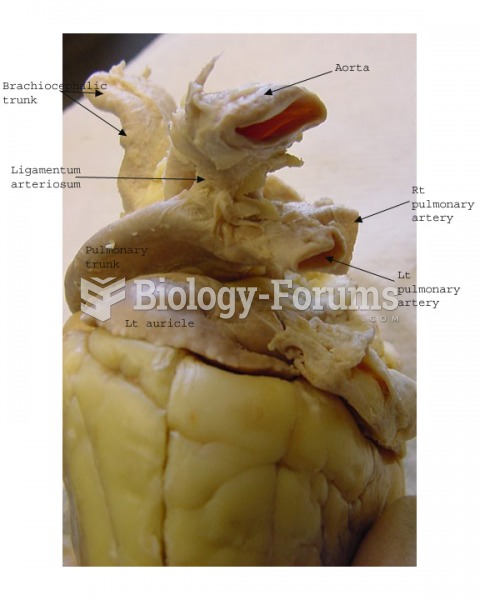
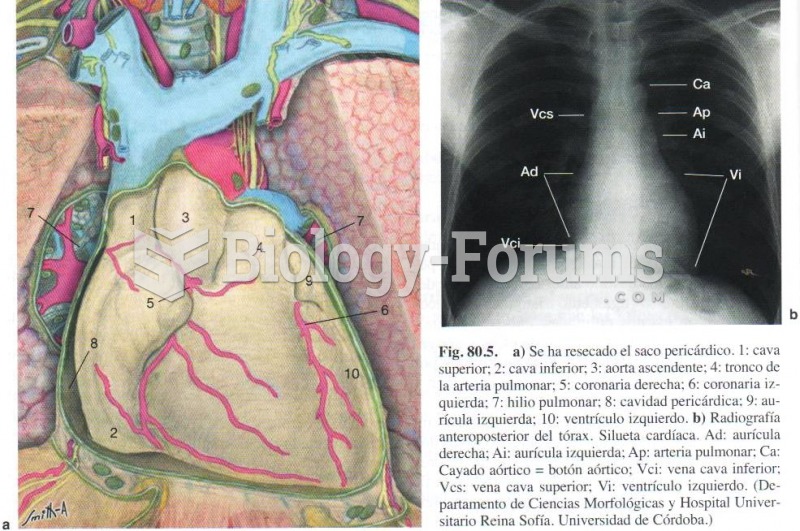
|
|
|
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
Barbituric acid, the base material of barbiturates, was first synthesized in 1863 by Adolph von Bayer. His company later went on to synthesize aspirin for the first time, and Bayer aspirin is still a popular brand today.
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.