|
|
|
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
About 80% of major fungal systemic infections are due to Candida albicans. Another form, Candida peritonitis, occurs most often in postoperative patients. A rare disease, Candida meningitis, may follow leukemia, kidney transplant, other immunosuppressed factors, or when suffering from Candida septicemia.
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
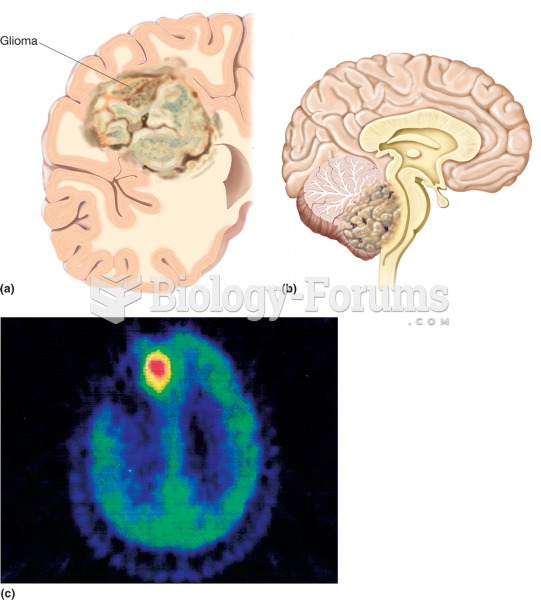
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").
Every flu season is different, and even healthy people can get extremely sick from the flu, as well as spread it to others. The flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May. Every person over six months of age should get an annual flu vaccine. The vaccine cannot cause you to get influenza, but in some seasons, may not be completely able to prevent you from acquiring influenza due to changes in causative viruses. The viruses in the flu shot are killed—there is no way they can give you the flu. Minor side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given. It is possible to develop a slight fever, and body aches, but these are simply signs that the body is responding to the vaccine and making itself ready to fight off the influenza virus should you come in contact with it.