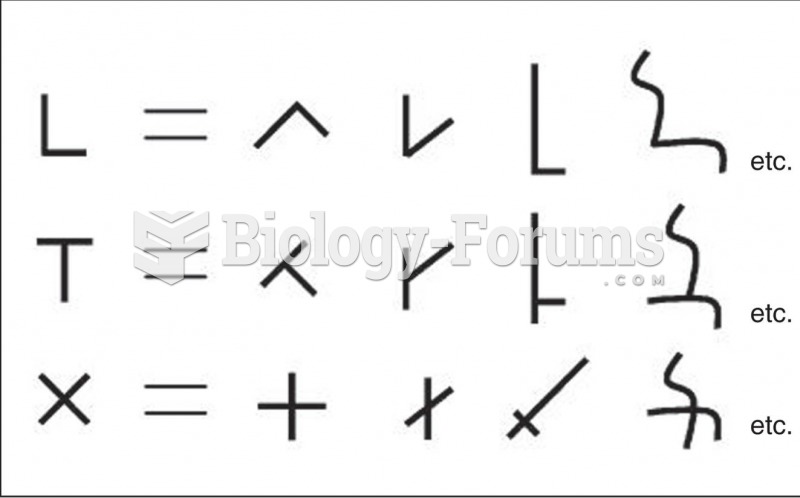
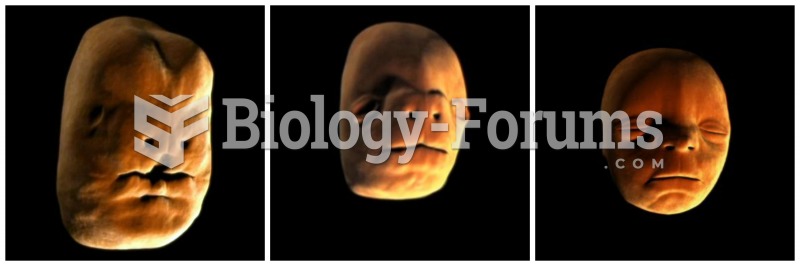
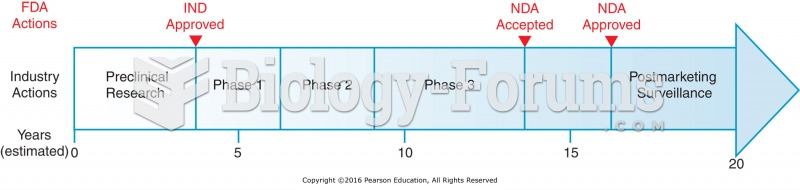
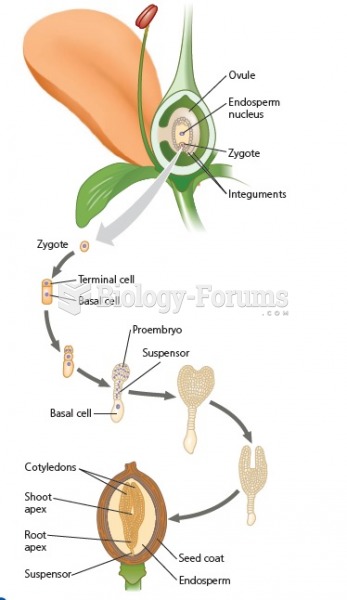
|
|
|
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
Disorders that may affect pharmacodynamics include genetic mutations, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's disease, and certain forms of insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus.
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.