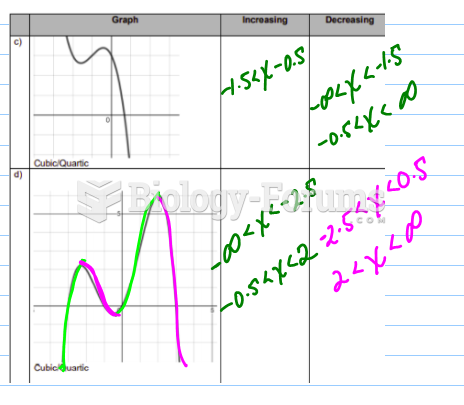
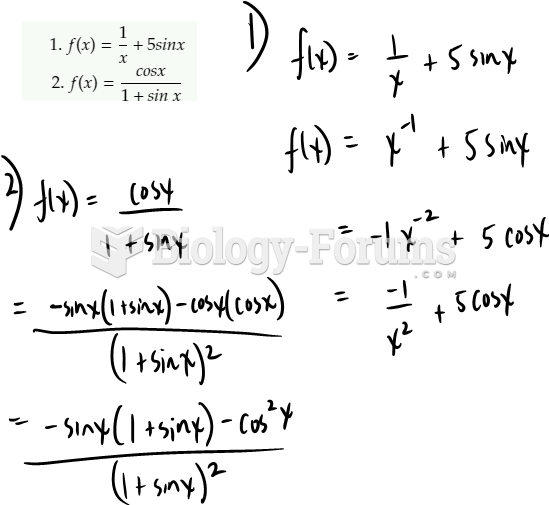
Answer to Question 1
The body contains about 100 milligrams of copper. About one-fourth is in the muscles; one-fourth is in the liver, brain, and blood; and the rest is in the bones, kidneys, and other tissues. The primary function of copper in the body is to serve as a constituent of enzymes. The copper-containing enzymes have diverse metabolic roles: they catalyze the formation of hemoglobin, help manufacture the protein collagen, inactivate histamine, degrade serotonin, assist in the healing of wounds, and help maintain the sheaths around nerve fibers. One of copper's most vital roles is to help cells use iron. Like iron, copper is needed in many reactions related to respiration and energy metabolism. The copper-dependent enzyme superoxide dismutase helps to control damage from free-radical activity in the tissues.
Answer to Question 2
Pronounced zinc deficiency is not widespread in developed countries, but deficiencies do occur in the most vulnerable groups of the U.S. populationpregnant women, young children, the elderly, and the poor. Even mild zinc deficiency can result in metabolic changes such as impaired immune response, abnormal taste, and abnormal dark adaptation (zinc is required to produce the active form of vitamin A, retinal, in visual pigments).
Some people are at greater risk of zinc deficiency than others. Pregnant teenagers need zinc for their own growth as well as for the developing fetus. Vegetarians whose diets emphasize whole grains, legumes, and other plant foods may also be at risk. These foods, though rich in zinc, also contain phytate, a potent inhibitor of zinc absorption. Protein enhances zinc absorption, but most plant-protein foods also contain phytate. The DRI committee suggests that the dietary zinc requirement for vegetarians who exclude all animal-derived foods may be as much as 50 percent greater than the RDA, but so far evidence is insufficient to establish zinc recommendations based on the presence of other food components or nutrients. Vegetarians who include cheese, eggs, or other animal protein in their diet absorb more zinc than those who exclude these foods.