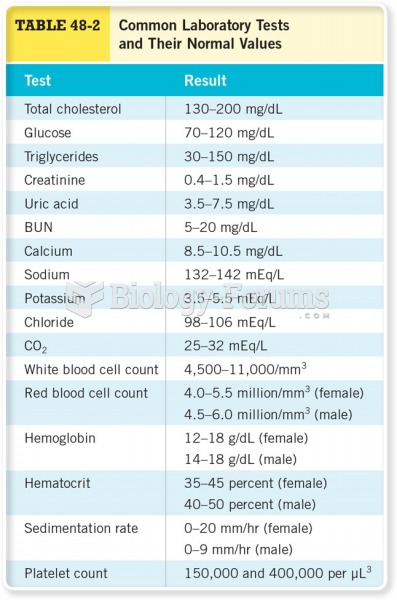
Answer to Question 1
High K due to tissue destruction, shock, acidosis, dehydration, and inadequate kidney function
High BUN due to hypercatabolism and the acute assault to his kidneys
High Cr due to AKI. Creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine (a part of muscle) that can be produced as a result of the acute assault to the kidney; there is also a lot of nitrogenous waste accumulation currently.
Low GFR (8 mL/min./1.73 m2): the most common measurement of kidney function, which is reflected in clearance tests. This measures the rate at which substances are cleared from the plasma by the glomeruli; normal GFR is 135-200 liters/day, of which 98-99 is reabsorbed with urine output. This is low most likely due to the low renal blood supply or damage from the infection causing the kidney dysfunction.
High glucose due to the patient's history of diabetes, as well as the acute infection and recent events (MI, surgery) that cause systemic stress and decreased glucose utilization (insulin resistance due to AKI).
High phosphorus is common with insufficient kidney function because the kidneys cannot filter this electrolyte as efficiently. Thus, phosphate and potassium are the most common electrolyte imbalances. These electrolyte imbalances are probably not due to excessive protein intake based on the low protein value and documented low PO intake.
Low protein could be due to excessive fluid (present edema) and protein losses due to kidney dysfunction
Low albumin due to fluid overload (present edema), the inflammatory response from the infection and protein losses due to kidney dysfunction
Low prealbumin due to fluid overload (present edema), the inflammatory response from the infection and protein losses due to kidney dysfunction
Low RBC count due to blood loss from recent surgery
Low hemoglobin/mean cell hemoglobin/mean cell hemoglobin content due to fluid overload (present edema), blood loss from recent surgery
Low hematocrit due to a possible underlying anemias, blood loss (from surgery)
High RBC distribution due to underlying anemia
Answer to Question 2
Abdominal obesity (waist circumference: > 40 (102 cm) and > 35 (88 cm) in men and women, respectively)
Atherogenic dyslipidemia ( triglycerides 150 mg/dL, HDL-cholesterol < 40 mg/dL and < 50 mg/dL in men and women, respectively)
Elevated blood pressure 130/85 mmHg
Insulin resistance glucose intolerance (FPG > 100 mg/dL)
Proinflammatory state
Prothrombotic state