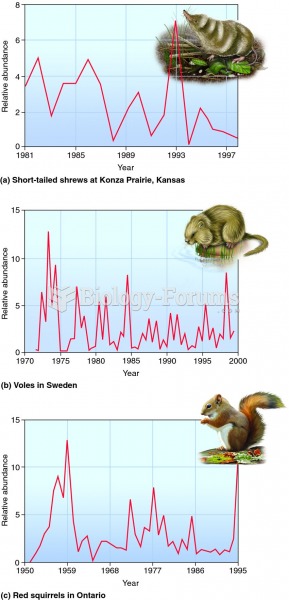
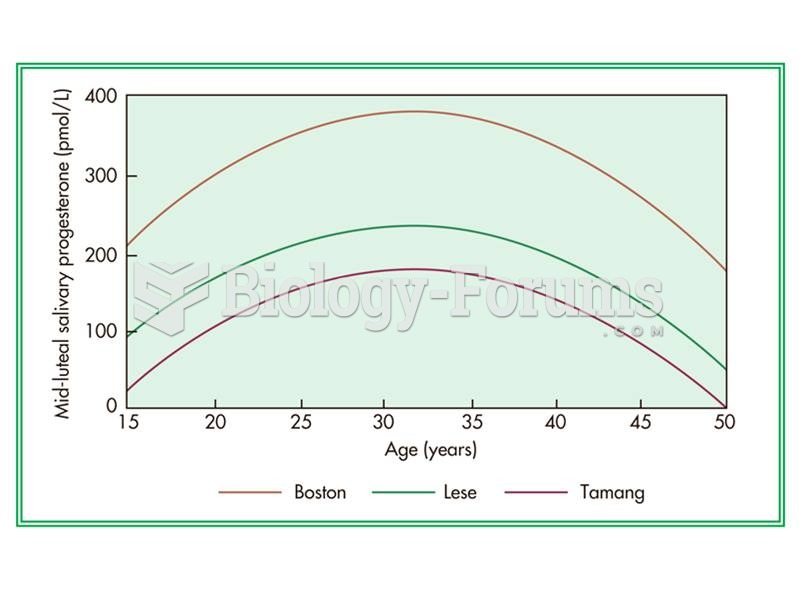
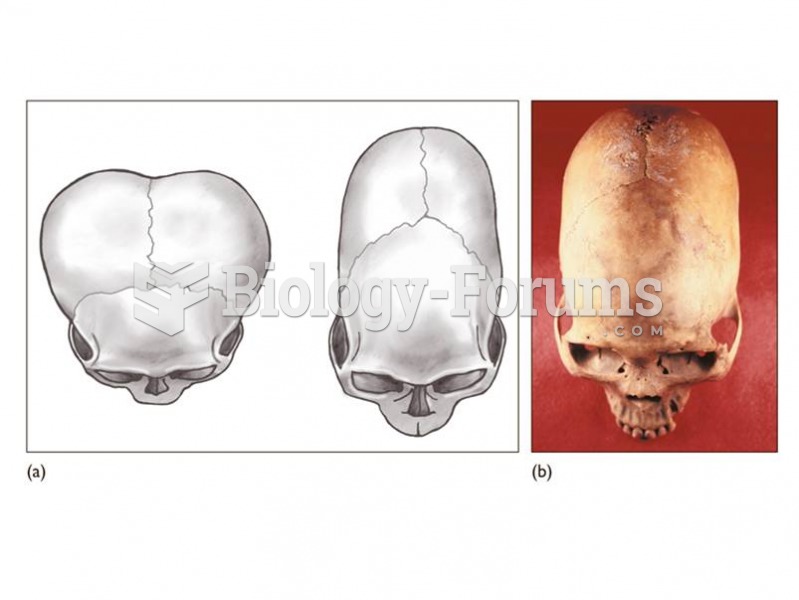
|
|
|
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.