|
|
|
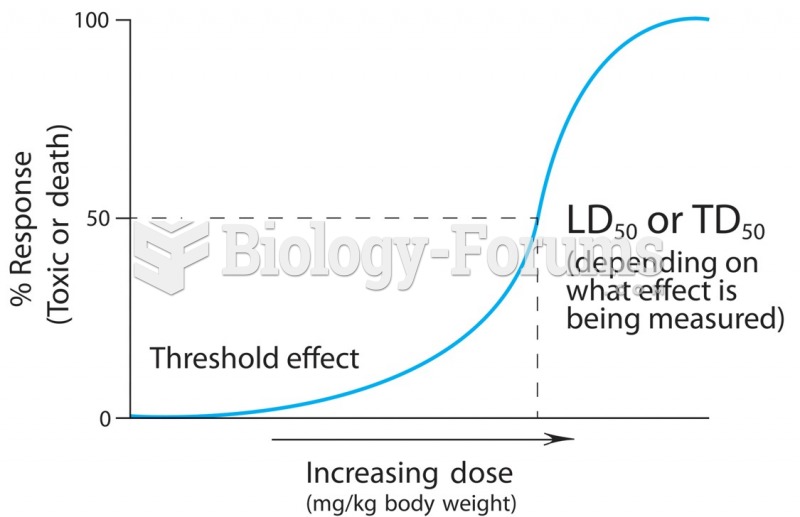
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.