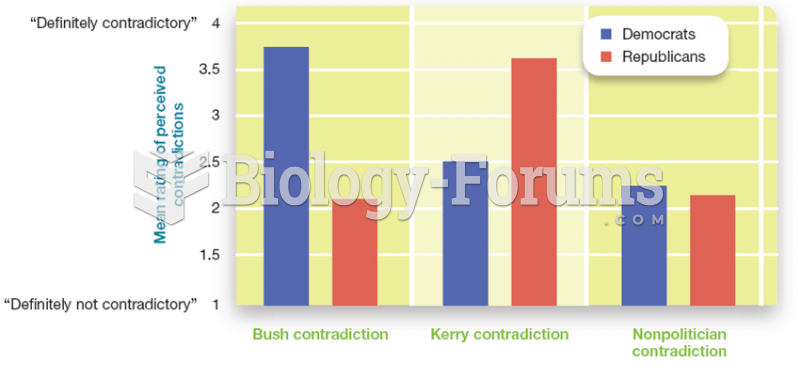
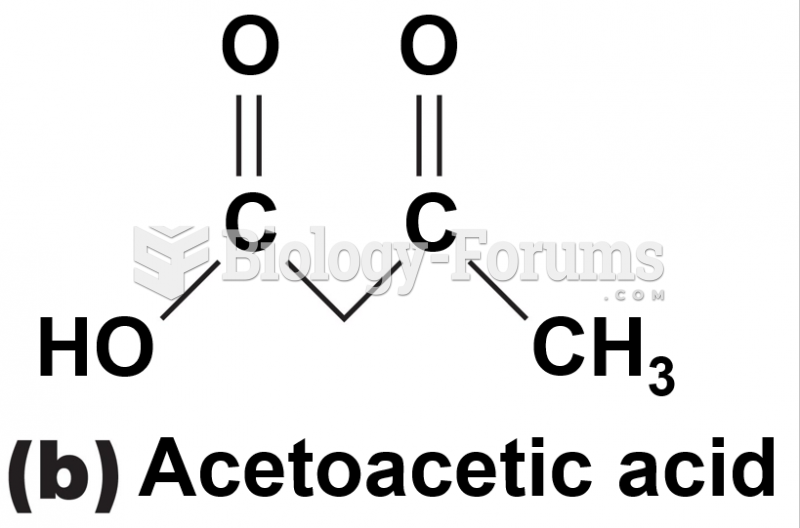
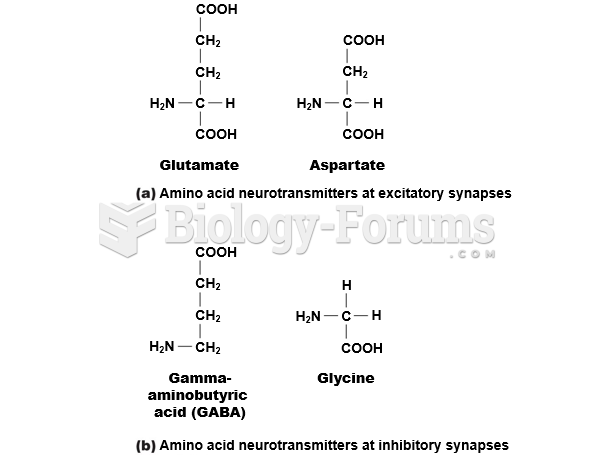
|
|
|
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.
Adolescents often feel clumsy during puberty because during this time of development, their hands and feet grow faster than their arms and legs do. The body is therefore out of proportion. One out of five adolescents actually experiences growing pains during this period.
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).