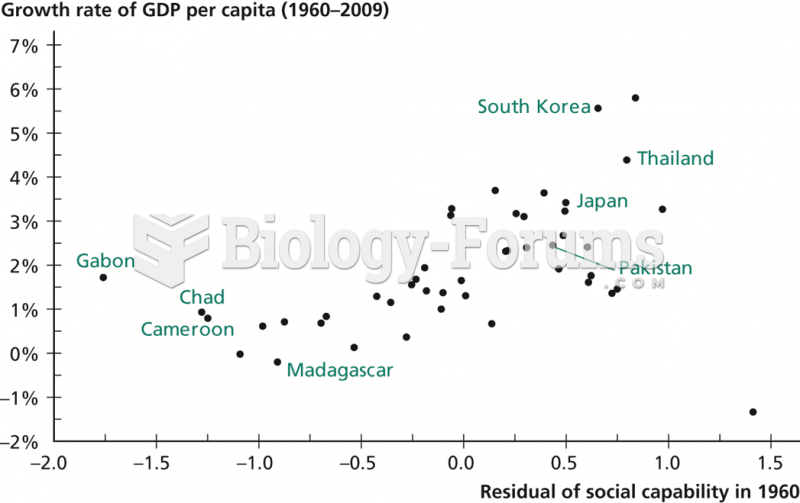
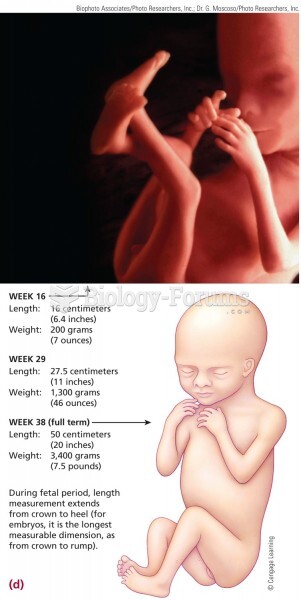
|
|
|
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
A headache when you wake up in the morning is indicative of sinusitis. Other symptoms of sinusitis can include fever, weakness, tiredness, a cough that may be more severe at night, and a runny nose or nasal congestion.
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.
 A page from Kelileh o Demneh dated 1429, from Herat, a Persian translation of the ancient Indian Pan
A page from Kelileh o Demneh dated 1429, from Herat, a Persian translation of the ancient Indian Pan
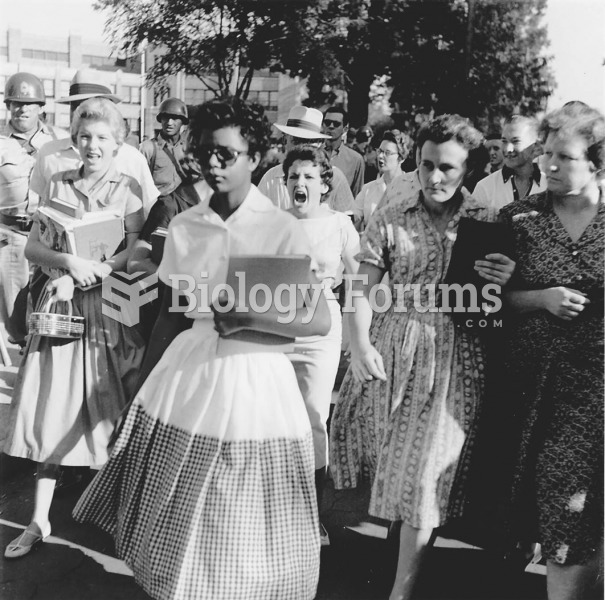
 The world has been horrified recently at a U.S. Congress so polarized and paralyzed that it cannot p
The world has been horrified recently at a U.S. Congress so polarized and paralyzed that it cannot p
 In 1891 William Dean Howells championed the poetry of Emily Dickinson: “This poetry is as characteri
In 1891 William Dean Howells championed the poetry of Emily Dickinson: “This poetry is as characteri