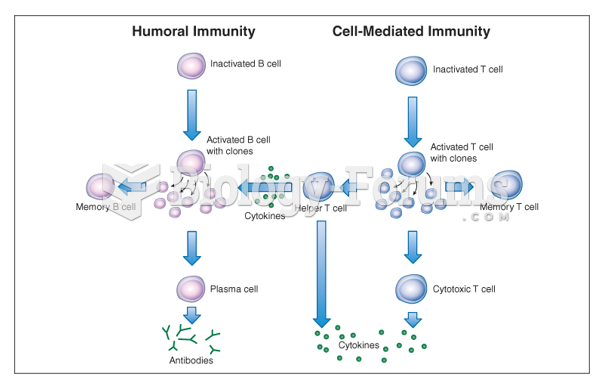
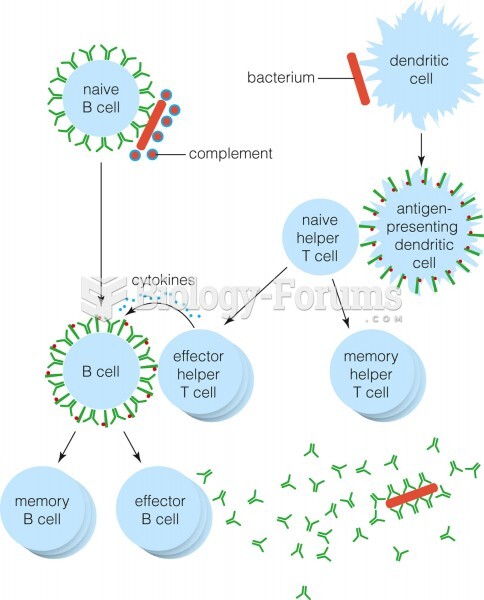
Answer to Question 1
In response to the physical demands of frequent exercise, the body undergoes physiologic adaptations that help to improve overall health and fitness. This adaptation response helps the body respond to the rigors of exercise more efficiently and forcefully. The muscles become larger and stronger, or undergo what is referred to as hypertrophy, and develop a higher tolerance for lactate, while the cardiovascular system increases its capacity for oxygen delivery. This is why it is important for athletes to train in order to optimize athletic performance.
Answer to Question 2
Benefits of exercise on health and fitness include the following:
Weight Management. Regular physical activity helps to increase muscle mass and decrease body fat. It also increases energy expenditure and helps regulate appetite. When combined with a healthy diet, physical activity can promote weight loss and help prevent unwanted weight gain.
Prevention of High Blood Pressure. Physical activity helps to strengthen the heart and lungs, which in turn can help control and in some cases reduce blood pressure in hypertensive individuals. Weight loss associated with physical activity can help lower body weight, which in turn can lower blood pressure.
Decreased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. In addition to strengthening heart muscles, physical activity can help lower resting heart rate, and improve healthy blood lipids by lowering triglycerides and LDL-cholesterol and raising HDL-cholesterol. These beneficial changes help slow the progression of atherosclerosis, maintain healthy blood pressure, and help the heart to function more efficiently.
Reduced Risk of Cancer. Because being overweight increases a person's risk of developing certain forms of cancer (breast, colorectal, pancreatic, uterine, esophageal, and kidney), a combination of a healthy diet and physical activity can help you to reduce your risk for these types of cancer through maintenance of a healthy body weight.
Decreased Back Pain. Exercise can increase muscle strength, endurance, flexibility, and overall posture, all of which can help prevent injuries and alleviate back pain associated with muscle strain.
Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Regular physical activity can help decrease blood glucose, insulin resistance, and long-term health complications associated with type 2 diabetes. In addition, physical activity can help prevent and control this type of diabetes by helping maintain a healthy body weight. In some cases, exercise can reduce insulin requirements for those with insulin-requiring diabetes.
Optimized Bone Mass. Weight-bearing physical activity can stimulate bone formation and slow the progression of age-related bone loss. Because physical activity can improve muscle strength and flexibility, staying physically active can reduce the likelihood of injuries when falls occur.
Enhanced Self-Esteem, Stress Management, and Quality of Sleep. Being physically active provides a sense of achievement and empowerment. This can help reduce depression and anxiety, which in turn can foster improved self-esteem. Regular physical activity provides a positive and effective means to manage stress, and can even improve mood and promote restful sleep.