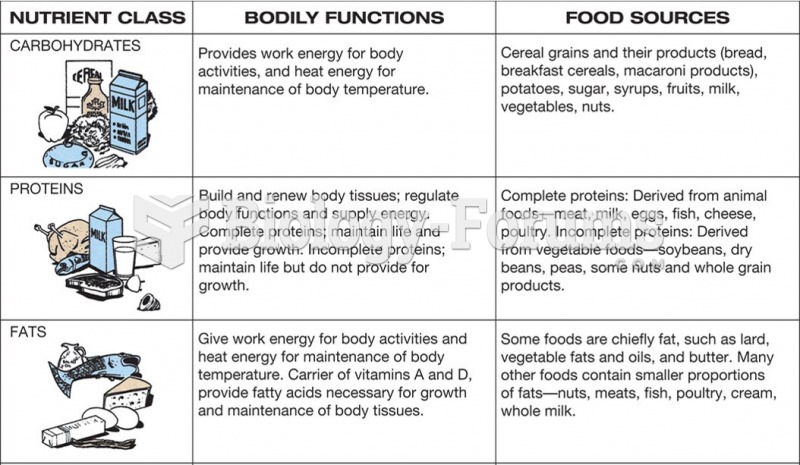
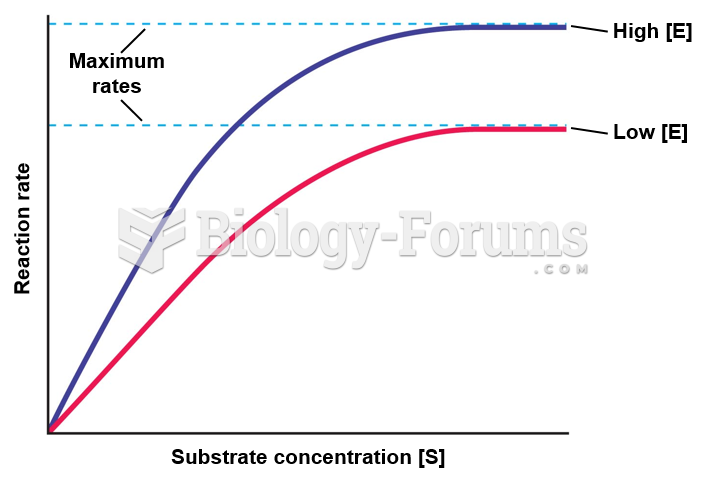
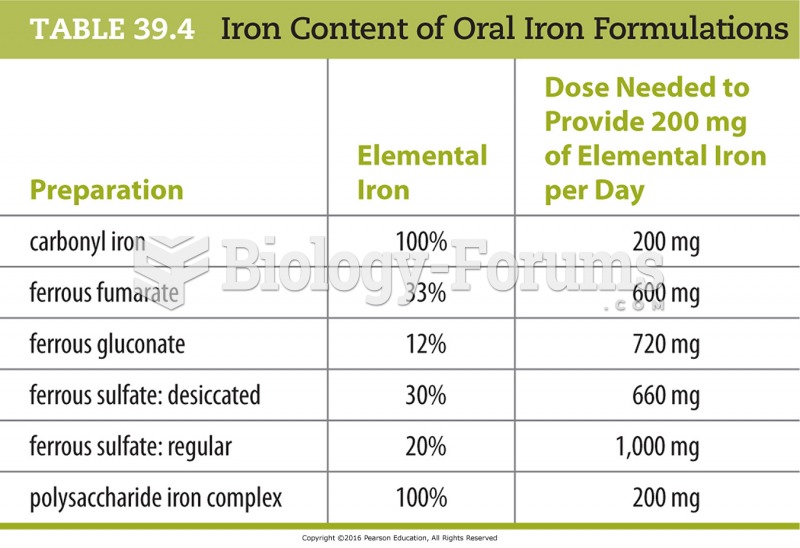
|
|
|
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.