Types of antimicrobial substances (interferons & complement protein)
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/25/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Types of antimicrobial substances interferons complement protein interstitial fluids phagocytosis cytolysis antigen antibody membrane attack complex
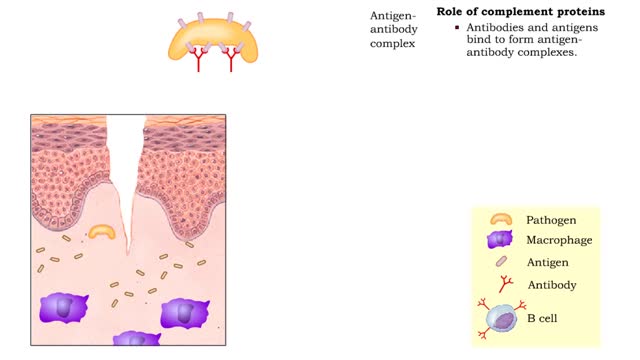
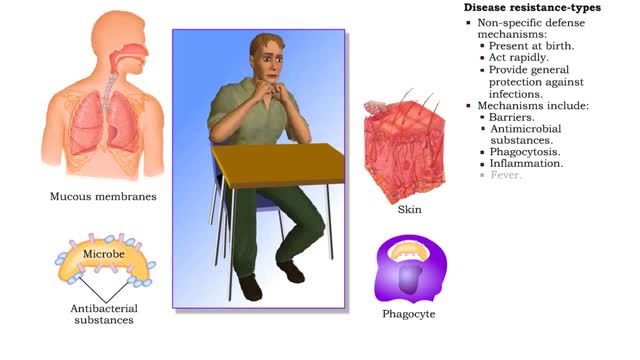
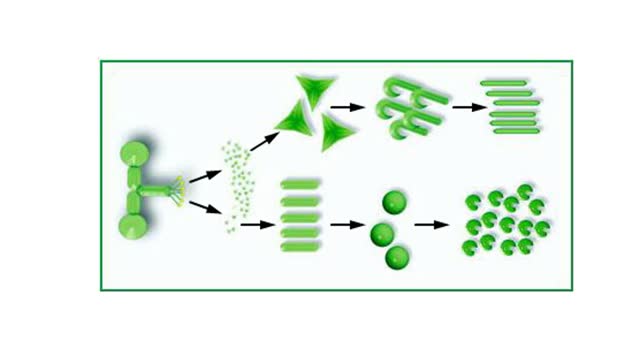
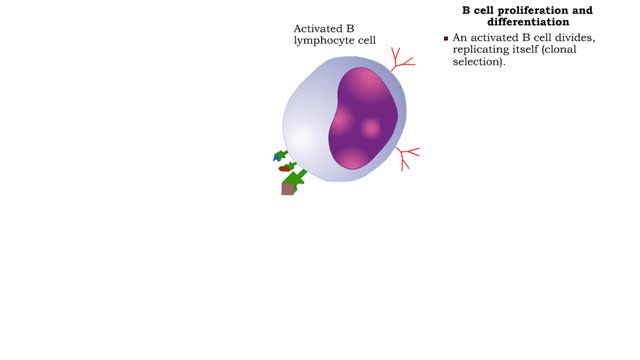
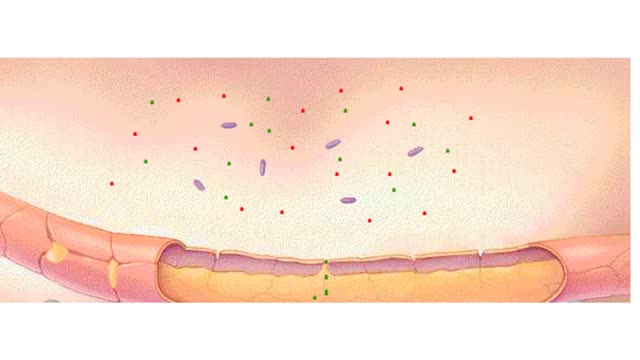
• Found in blood and interstitial fluids. • Discourage microbial growth. • Include interferon and complement proteins. • Produced and released by virus-infected lymphocytes. • Enter new cells and inhibit viral replication. • Act against a large variety of viruses (non-specific). • Form the complement system, a group of inactive plasma proteins. • Enhance phagocytosis, inflammation and cytolysis. • Production is triggered by formation of antigen-antibody complexes. • Classical complement pathway: • Begins with Cl binding to antigen-antibody complex. • Continues with the formation of C3a, C4a, C5a, C3b, and other proteins. • Enhances inflammation, which helps tissue resist disease and heal. • Forms complexes such as the membrane attack complex (MAC) that perforates the membranes of microbes, promoting cytolysis. • Alternative complement pathway: • Begins with direct contact between complement protein and microbe. • Complement proteins coat the microbe surface, promoting adherence to phagocytes.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.