Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 02/10/2020
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Glucose glycolysis Krebs Cycle electron transport chain cytoplasm mitochondria ATP
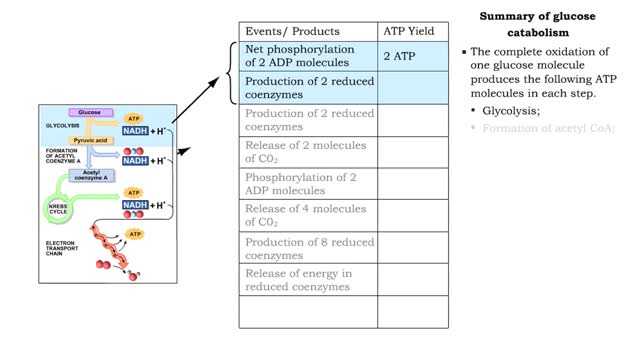
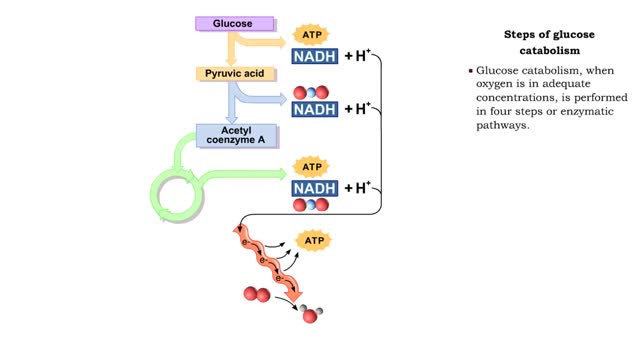
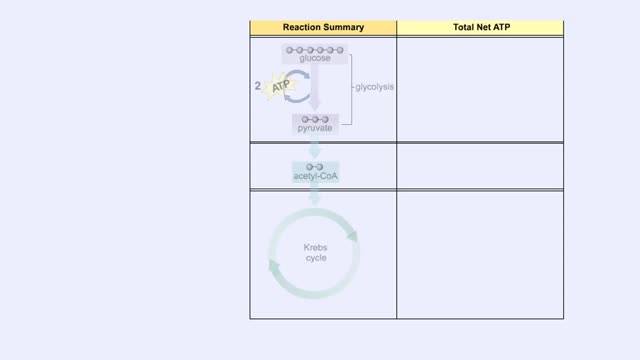
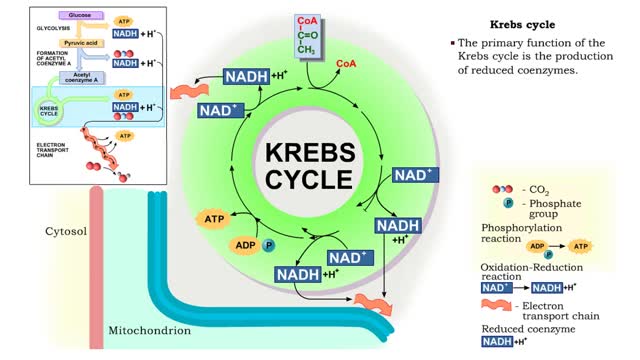
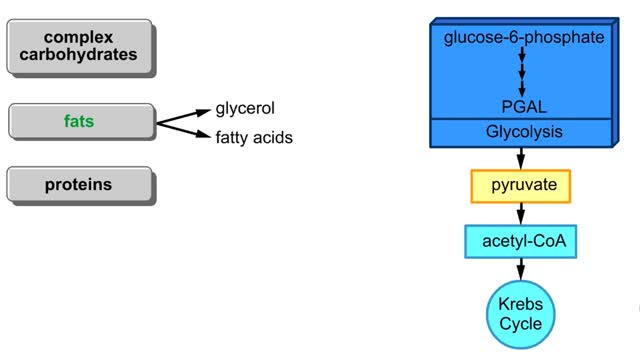
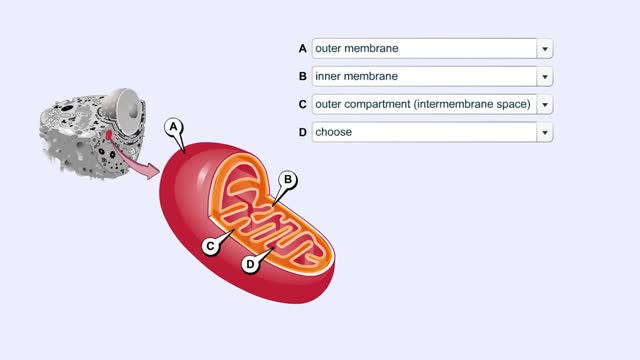
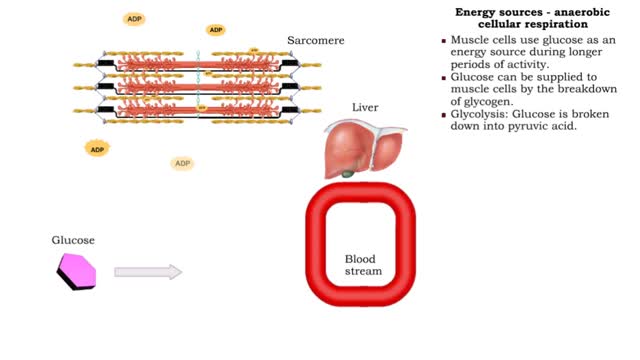
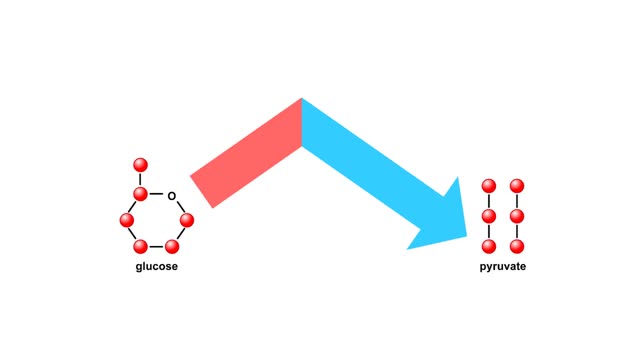
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as glycolysis. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm while the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain reactions occur in the mitochondria. Glucose enters the cell from the blood stream through a protein transport molecule in the plasma membrane. Once inside the cell, it enters the glycolysis pathway. The first step in glycolysis is the addition of a phosphate group to the number 6 carbon of glucose. A molecule of ATP is utilized. Glucose is transformed into glucose-6-phosphate. Energy, in the form of a molecule of ATP, must actually be used to begin the glycolysis pathway. During the addition of these phosphate groups, a slight rearrangement of the sugar occurs so that the resulting molecule is now fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Two ATP molecules have now been used up, so we have a deficit in our ATP account which will be made up shortly.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.