 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
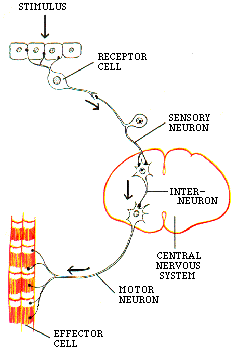
| Description: sensory neuron = afferent neuron - A neuron conducting sensory information from a receptor cell or organ in the form of nerve impulses inwards to nerve centers in the brain or spinal cord (central nervous system). motor neuron = efferent neuron - A neuron which conveys impulses outward from the brain or spinal cord (central nervous system) to regulate the action of a muscle, gland, or other effector tissue. interneuron = association neuron - A nerve cell found entirely within the central nervous system that acts as a link between sensory neurons and motor neurons or connects with other interneurons in a network or pathway within the CNS. unipolar neuron - One of the structural classifications of neurons: a neuron from which only a single process leaves the cell body; this single process then divides close to the cell body into a trunk to supply the branching dendrites for incoming signals and an axon for outgoing signals; unipolar neurons are typically sensory neurons with receptors located within the skin, joints, muscles, and internal organs; their axons are usually long, terminating in the spinal cord, while the length of their dendritic trunks vary. bipolar neuron - One of the structural classifications of neurons: a neuron from which two processes leave the cell body; in this neuron, the dendritic tree emerges from one end of the cell body, while the axon emerges from the opposite end; the dendritic branching of bipolar neurons is typically limited, and the axons of such neurons are usually short in length. (Bipolar neurons are often sensory neurons associated with receptor organs of the visual and auditory systems. The narrow fields created by the short dendrites of these neurons underlie the concise encoding of visual and auditory information representing physical signals from the external world. Without this narrow encoding of sensory information, the resolution of vision and hearing would be reduced.) multipolar neuron - One of the structural classifications of neurons: a neuron from which multiple branches leave the cell body; the many dendrites of the multipolar neuron allow for extensive integration of information coming from many other neurons; the axons of such neurons are usually long, allowing this integrated information to affect distant regions of the nervous system. (The majority of neurons.) presynaptic neuron* - A relative term used to identify the limited relationship between any two neurons in communication; the presynaptic neuron is the message sender and it will have its axon terminal in synapsis with the postsynaptic neuron which is the message receiver; it will release a neurotransmitter to stimulate (excite or inhibit) the postsynaptic neuron. postsynaptic neuron* - A relative term used to identify the limited relationship between any two neurons in communication; the postynaptic neuron is the message receiver and its cell membrane will be in synapsis with the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron which is the message senderr; it will receive a neurotransmitter to stimulate (excite or inhibit) from the presynaptic neuron and it will release a neurotransmitter to stimulate (excite or inhibit) the next cell or cells (neuron or effector) in the pathway. Picture Stats: Views: 1055 Filesize: 8.59kB Height: 352 Width: 237 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=16261 |
