 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
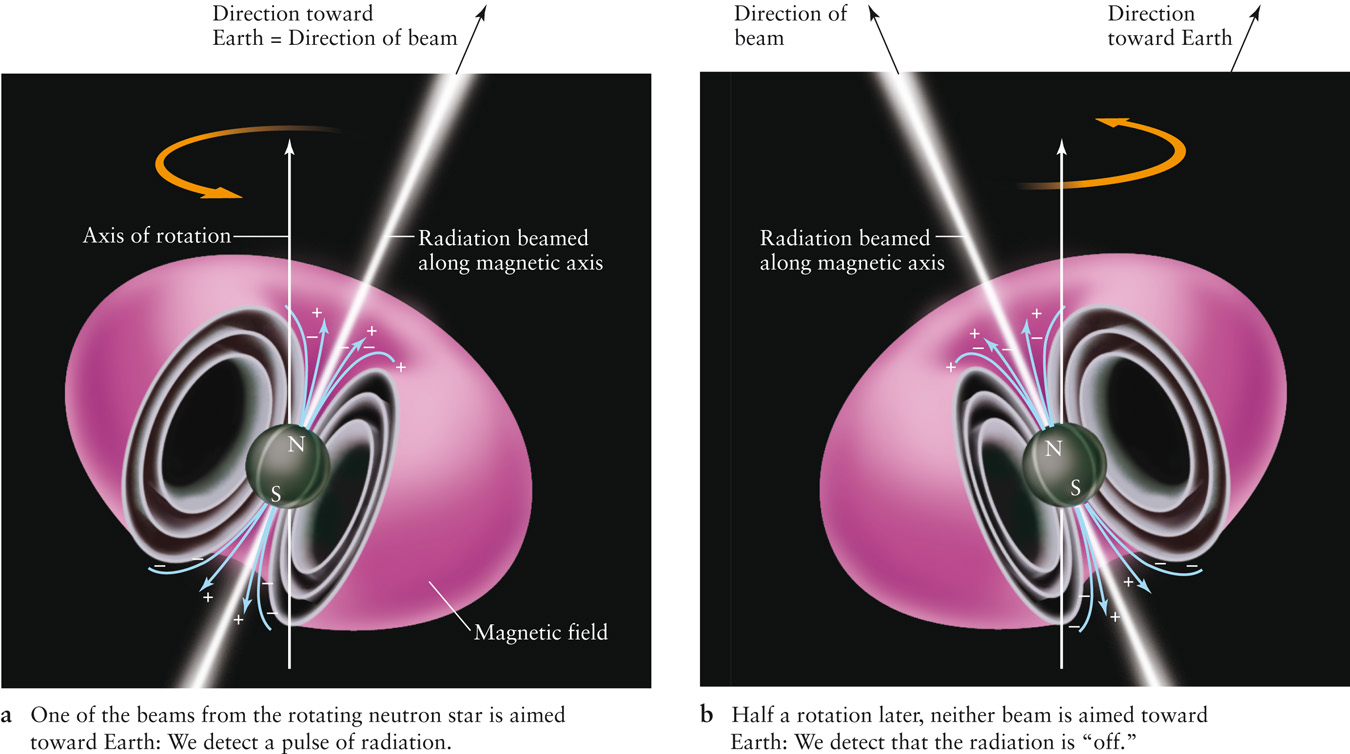
| Description: A Rotating, Magnetized Neutron Star Calculations reveal that many neutron stars rotate rapidly and possess powerful magnetic fields. Charged particles are accelerated near a neutron star’s magnetic poles and produce two oppositely directed beams of radiation. As the star rotates (going from a to b is half a rotation period), the beams sweep around the sky. If Earth happens to lie in the path of a beam (a, but not b), we see the neutron star as a pulsar. Picture Stats: Views: 742 Filesize: 204.46kB Height: 754 Width: 1350 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=18629 |
