 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
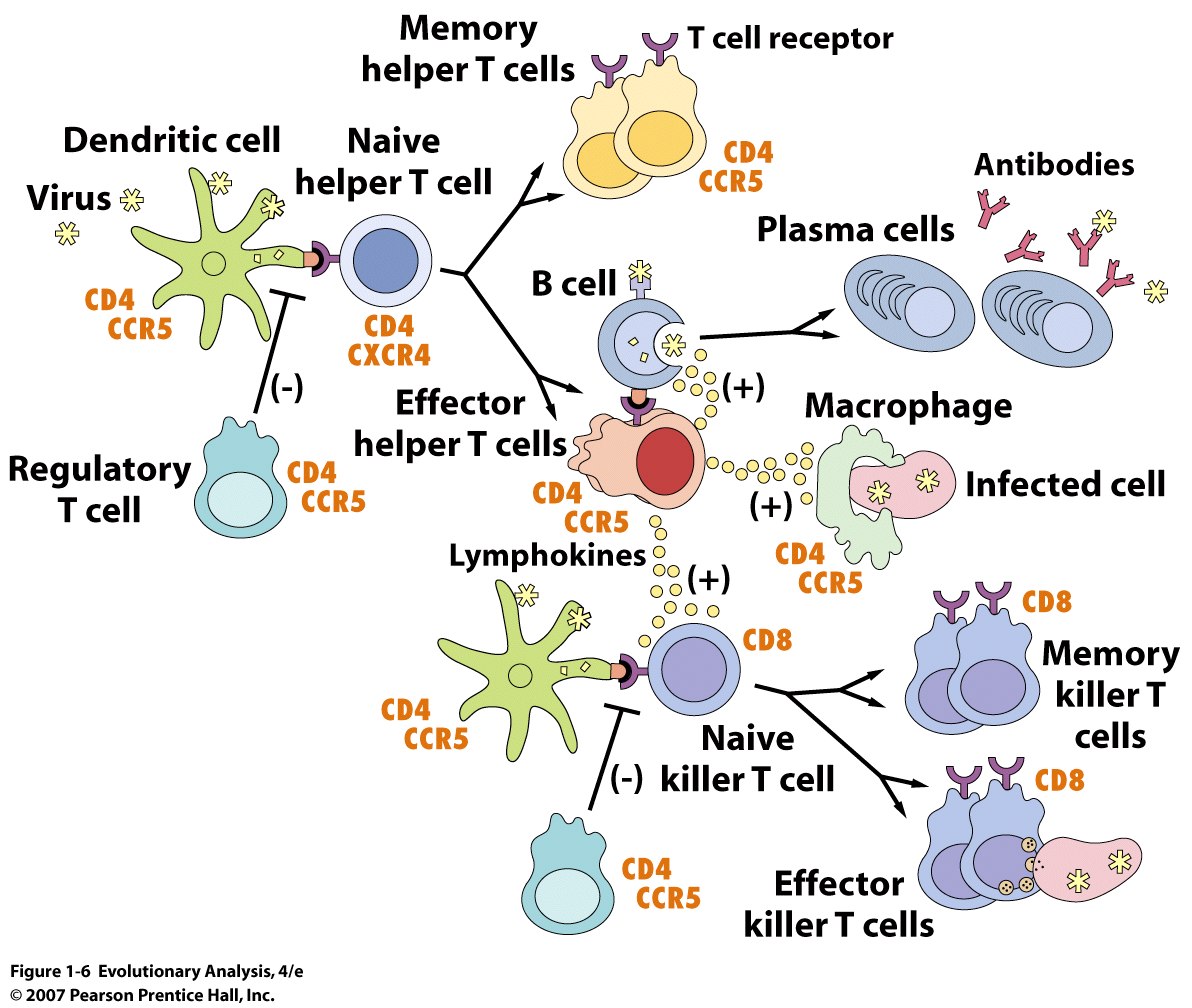
| Description: Dendritic cells (green) take up the virus and present bits of its proteins to naive helper T cells. Once activated by a bit of viral protein that fits its T cell receptor, a helper T cell divides to produce memory cells (yellow) and effector cells (red). Memory helper T cells sit out the current battle but remain ready to trigger a quick reaction should the same virus invade again. Effector helper T cells join the current fight. In part by releasing signalling molecules called chemokines, they stimulate B cells to mature into plasma cells that produce antibodies that bind the virus. Effector helper T cells also stimulate macrophages to ingest infected cells and help activate naive killer T cells. Activated killer T cells divide to produce memory cells and effector cells. Effector killer T cells identify and kill cells infected with the invading virus. The immune response is kept under control by regulatory T cells. The orange labels identify cell-surface proteins, some of which are exploited by HIV to gain entry into cells. Modified from NIAID (2003).
Picture Stats: Views: 1610 Filesize: 199.49kB Height: 1008 Width: 1192 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=1908 |
