 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
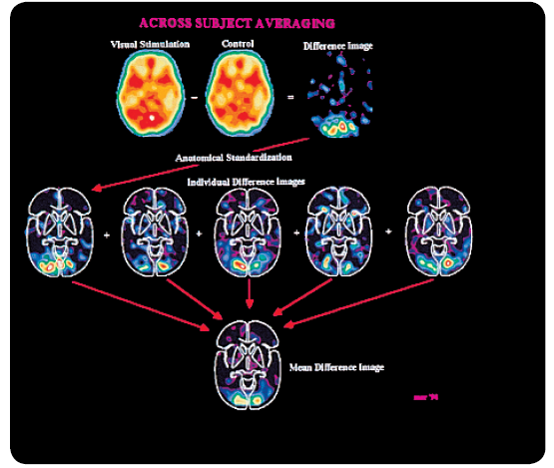
| Description: The paired-image subtraction technique, which is commonly employed in cognitive neuroscience. Here we see that the brain of a subject is generally active when the subject looks at a flickering checkerboard pattern (visual stimulation condition). However, if the activity that occurred when the subject stared at a blank screen (control situation) is subtracted, it becomes apparent that the perception of the flashing checkerboard pattern was associated with an increase in activity that was largely restricted to the occipital lobe. The individual difference images of five subjects were averaged to produce the mean difference image. (PET scans courtesy of Marcus Raichle, Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University Medical Center.)
Picture Stats: Views: 2798 Filesize: 193.4kB Height: 468 Width: 554 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=30285 |
