 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
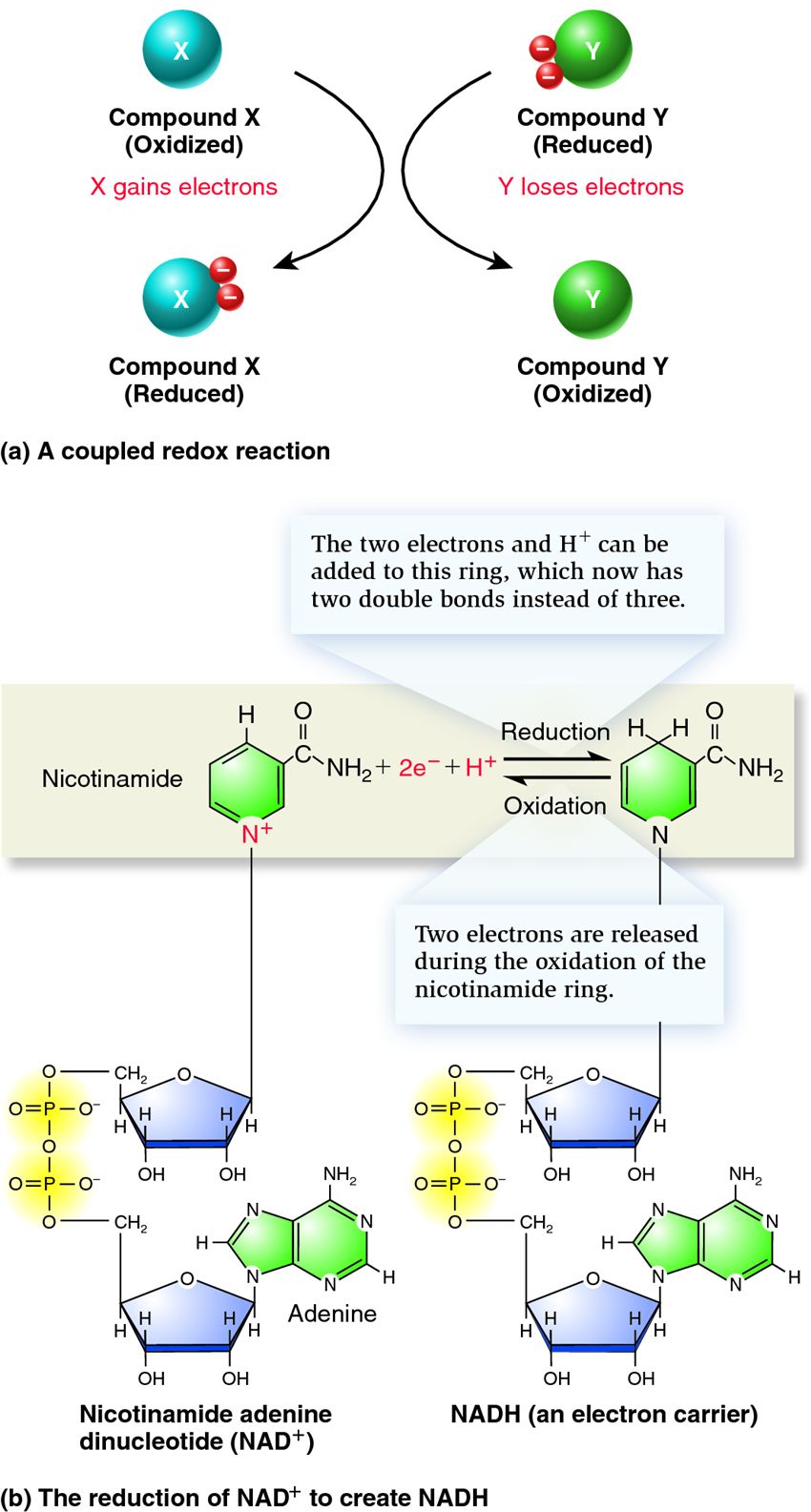
| Description: (a) Oxidized compound X receives electrons from reduced compound Y. In this case, Y serves as a reducing agent, and upon donating its electrons, it becomes oxidized. Y can now serve as an oxidizing agent, capable of receiving electrons from a reduced compound (not necessarily X). (b) NAD+ is composed of two nucleotides, one with an adenine base and one with a nicotinamide base. The oxidation of organic molecules releases electrons that can bind to NAD+ and (along with a hydrogen ion) result in the formation of NADH. The two electrons and H+ are incorporated into the nicotinamide ring. Note: The actual net charges of NAD+ and NADH are minus one and minus two, respectively. They are designated NAD+ and NADH to emphasize the net charge of the nicotinamide ring, which is involved in many oxidation–reduction reactions.
Picture Stats: Views: 1318 Filesize: 143.53kB Height: 1585 Width: 850 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=323 Keywords: Redox reactions |
