 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
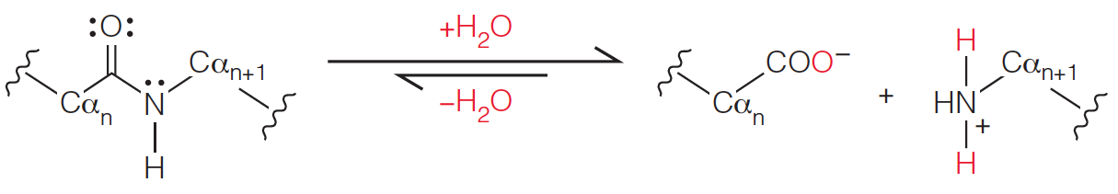
| Description: While hydrolysis of peptide bonds is thermodynamically favored in aqueous solutions, the reaction is exceedingly slow at physiological pH and temperature Peptide bond hydrolysis can be achieved by: Strong mineral acid (e.g., 6 M HCl) cleaves all peptide bonds (including the Asn and Gln amide bonds) Chemicals that cleave at specific sites (e.g., CNBr cleaves at Met) Proteolytic enzymes (proteases) that cleave at specific sites Picture Stats: Views: 332 Filesize: 34.61kB Height: 194 Width: 1118 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=33920 |
