 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
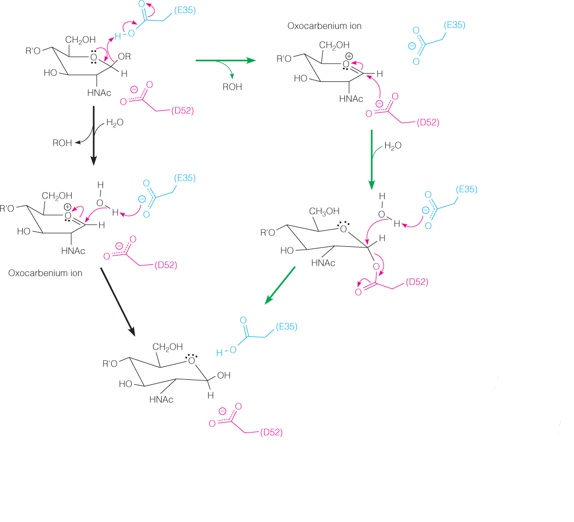
| Description: The Phillips mechanism is illustrated by the black reaction arrows along the left side of the diagram. In the first step, E35 acts as a general acid to promote cleavage of the glycosidic bond and concomitant formation of the oxocarbenium ion (which is stabilized electrostatically by D52). In the second step, E35 acts as a general base, deprotonating a water molecule, which then attacks C1 of the substrate. The pathway that includes the covalent intermediate reported by Steve Withers follows the green reaction arrows along the right side of the diagram. In this case, the second step involves covalent bond formation between C1 of the substrate and D52. Attack of the water displaces D52 in thesubsequent step. Picture Stats: Views: 339 Filesize: 149.46kB Height: 522 Width: 574 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=34375 |
