 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
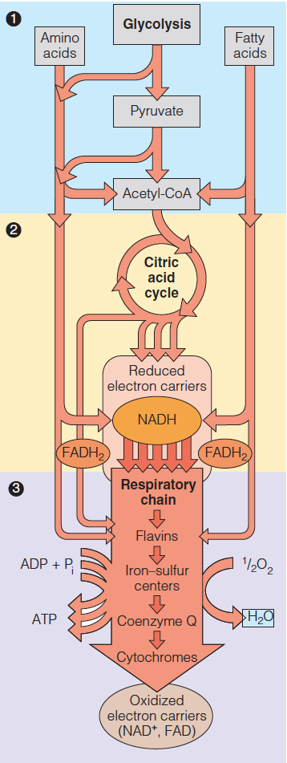
| Description: The average adult human synthesizes ATP at a rate of nearly 1021 molecules per second, equivalent to producing his or her own weight in ATP every day. Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle by themselves generate relatively little ATP directly. However, under aerobic conditions, six dehydrogenation steps: One in glycolysis One in pyruvate dehydrogenase Four in the citric acid cycle Collectively reduce 10 moles of NAD+ to NADH and 2 moles of FAD to FADH2 per mole of glucose. Reoxidation of these reduced electron carriers in the process termed cellular respiration generates most of the energy needed for ATP synthesis. Oxidation of 1 mole of NADH by the respiratory chain provides sufficient energy for synthesis of ~2.5 moles of ATP from ADP. Picture Stats: Views: 364 Filesize: 122.39kB Height: 763 Width: 287 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=34564 |
