 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
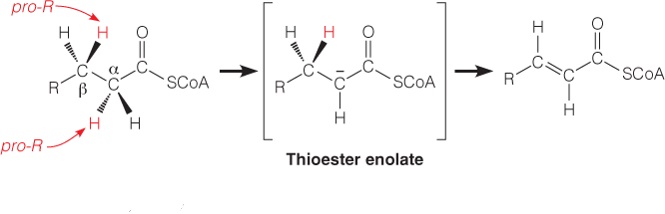
| Description: The first reaction is catalyzed by an acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the removal of two hydrogen atoms from the a- and b-carbons to give a trans a,b-unsaturated acyl CoA (trans-D2-enoyl-CoA) as the product. The pro-R hydrogen on the b-carbon is then transferred as a hydride equivalent to FAD to give the trans double bond and enzyme-bound FADH2. Picture Stats: Views: 315 Filesize: 67.38kB Height: 214 Width: 665 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=34627 |
