 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
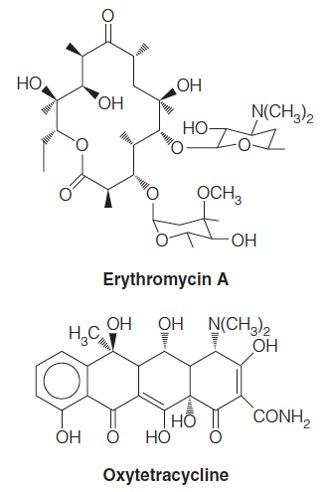
| Description: A related series of pathways in bacteria and fungi is involved in the biosynthesis of a class of antibiotics called polyketides. Examples include Erythromycin, from Saccharopolyspora erythraea, and oxytetracycline, from Streptomyces rimosus. These polyketide antibiotics are potent inhibitors of bacterial protein synthesis. Other polyketides, such as lovastatin and simvastatin have found clinical use as cholesterol-lowering drugs by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Polyketides are synthesized in assembly-line fashion by giant enzyme megasynthases that consist of individual modules for rounds of carbon addition, with each module closely resembling the process whereby two carbons are added in a cycle of the fatty acid synthesis pathway. Picture Stats: Views: 216 Filesize: 53.88kB Height: 492 Width: 328 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=34648 |
