 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
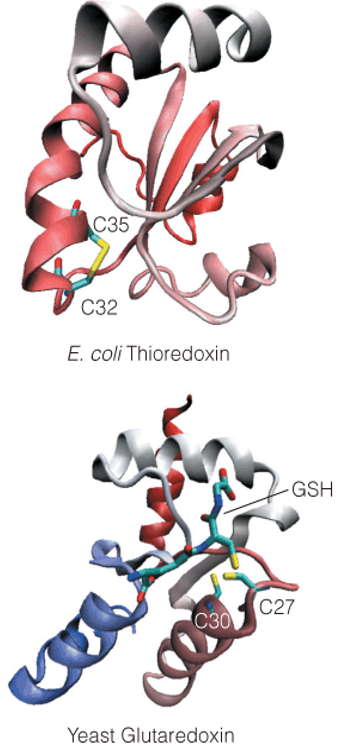
| Description: Ribonucleotide reductase uses a protein cofactor—thioredoxin or glutaredoxin—to provide electrons for reduction of the ribonucleotide substrate. However, the ultimate electron donor is NADPH. X-ray crystal structures of thioredoxin from E. coli and glutaredoxin from the yeast S. cerevisiae show the locations of the redox-active cysteine residues near their surfaces. In the thioredoxin structure, Cys32 and Cys35 are in the oxidized disulfide state. In the glutaredoxin structure, Cys27 and Cys30 are reduced, and a molecule of glutathione (GSH) is bound with its cysteinyl-SH adjacent to the two cysteine residues. Picture Stats: Views: 153 Filesize: 251.68kB Height: 755 Width: 351 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=34847 |
