 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
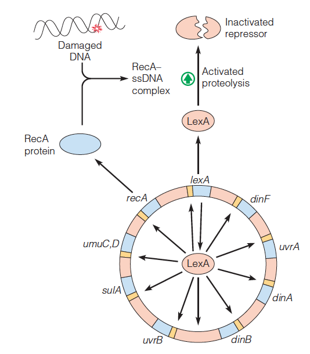
| Description: The figure shows locations on the E. coli chromosome of some of the genes controlled by the LexA repressor. dinA is the structural gene for DNA polymerase II. dinB encodes DNA polymerase IV. dinF is a damage-inducible gene of unknown function. umuC,D (so-called because mutants in this gene could not undergo ultraviolet mutagenesis) encodes the highly error-prone DNA polymerase V. LexA repressor (pink) is inactivated by proteolysis, which is somehow enhanced by a complex of RecA protein (blue) and single-strand DNA. The SOS regulon is activated by DNA damage, which stimulates RecA to cause proteolytic cleavage of the LexA and l cI repressors. Picture Stats: Views: 379 Filesize: 46.57kB Height: 354 Width: 310 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=35131 |
