 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
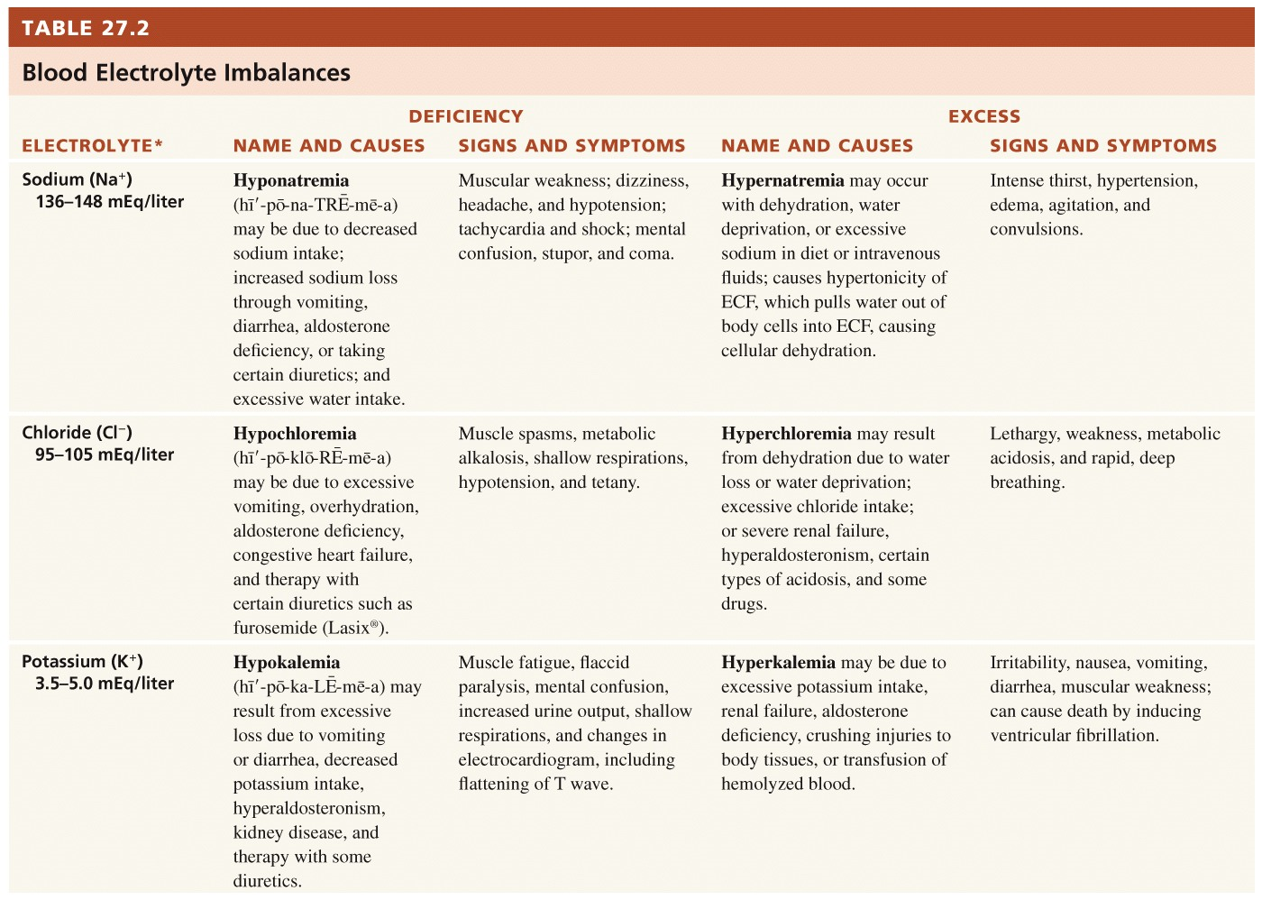
| Description: Sodium: most abundant cations in extracellular fluid - Used for impulse transmission, muscle contraction, fluid and electrolyte balance. - It’s level is controlled by aldosterone, ADH and ANP Chloride: the major extracellular anion - Helps regulate osmotic pressure between compartments - Forms HCl in the stomach - Regulation of Cl– balance is controlled by aldosterone Potassium: most abundant cation in intracellular fluid - Involved in fluid volume, impulse conduction, muscle contraction and regulating pH - Mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) regulate the plasma level Bicarbonate: important plasma ion - Major member of the plasma acid-base buffer system - Kidneys reabsorb or secrete it for final acid-base balance Calcium: most abundant mineral in the body - Structural component of bones and teeth - Used for blood coagulation, neurotransmitter release, muscle tone, excitability of nerves and muscles - Level in plasma regulated by parathyroid hormone Phosphate: occurs as calcium phosphate salt - Used in the buffer system - Regulated by parathyroid hormone and calcitriol Magnesium: an intracellular cation - Activates enzymes involved in carbohydrate and protein metabolism - Used in myocardial function, transmission in the CNS and operation of the sodium pump Picture Stats: Views: 211 Filesize: 885.3kB Height: 900 Width: 1262 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=40383 |
