 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
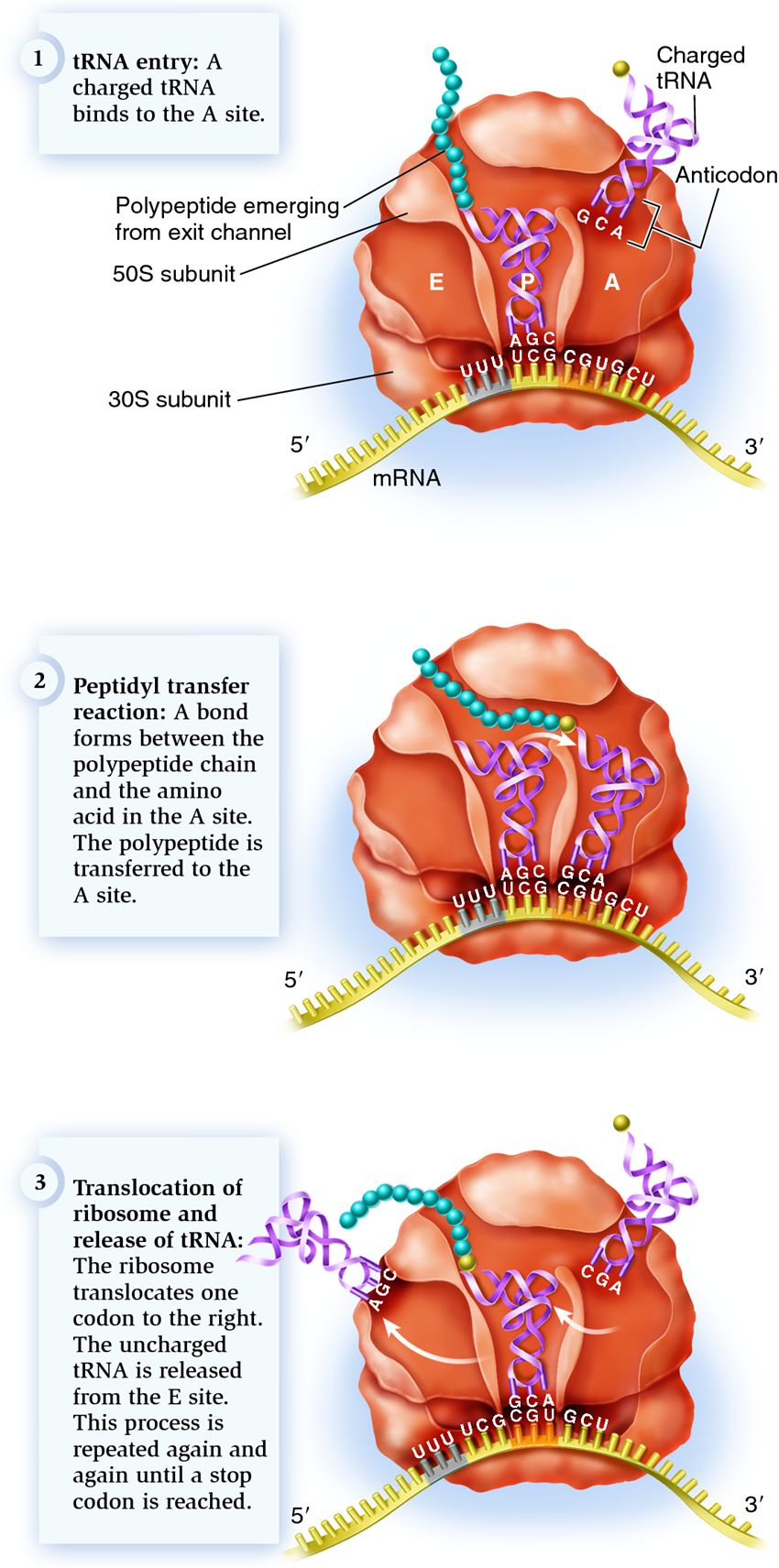
| Description: In the second step, a peptide bond is formed between the amino acid at the A site and the growing polypeptide chain, thereby lengthening the chain by one amino acid. As this occurs, the polypeptide is removed from the tRNA in the P site and transferred to the amino acid at the A site, an event termed a peptidyl transfer reaction. This reaction is catalyzed by a region of the 50S subunit known as the peptidyltransferase complex, which is composed of several proteins and rRNA. Thomas Steitz, Peter Moore, and their colleagues proposed that the rRNA is responsible for catalyzing bond formation between adjacent amino acids. In other words, the ribosome is a ribozyme.
Picture Stats: Views: 3491 Filesize: 190.7kB Height: 1712 Width: 850 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=436 Keywords: Elongation stage of translation in bacteria |
