 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
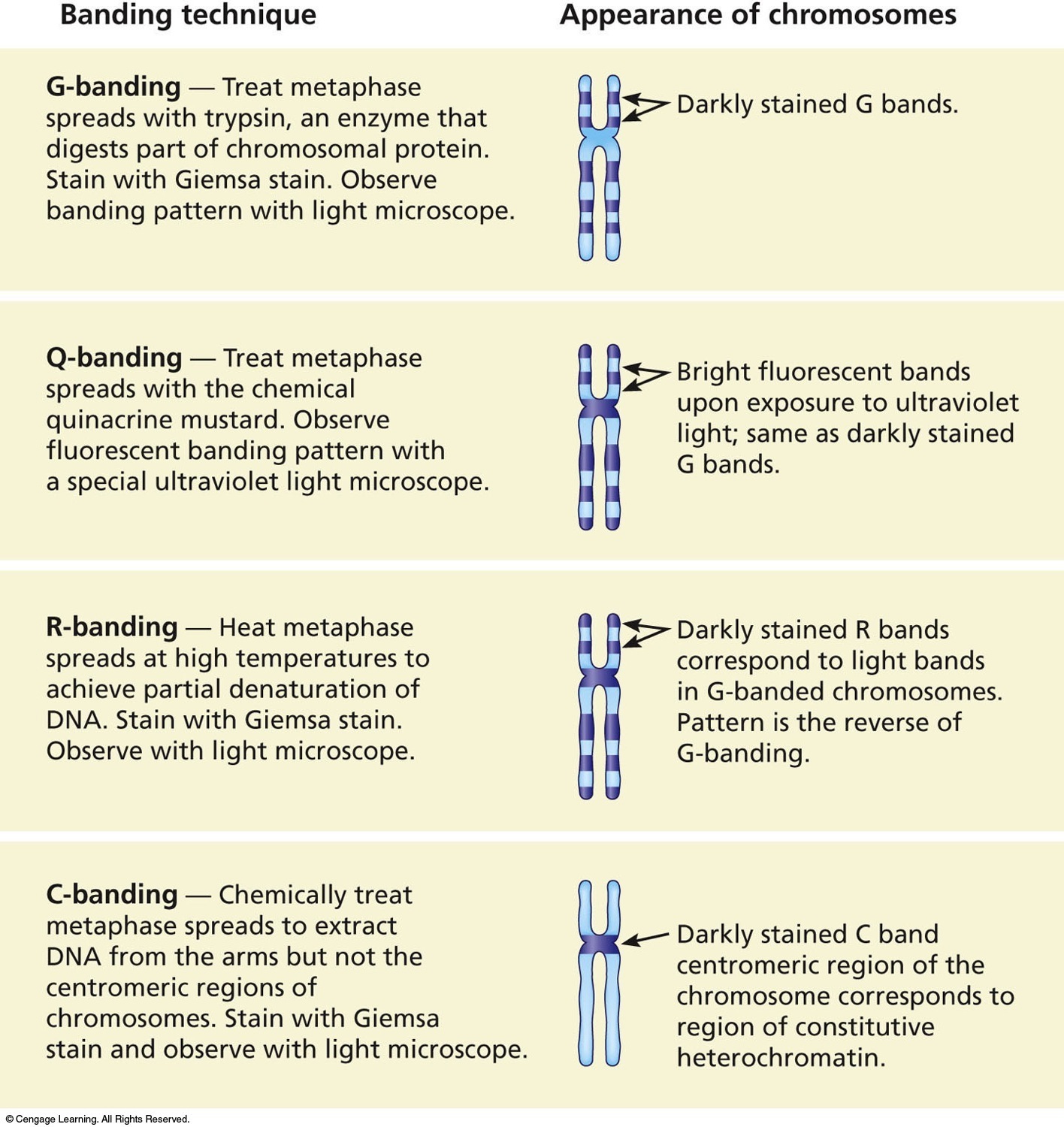
| Description: Four common staining procedures used in chromosomal analysis. Most karyotypes are prepared using G-banding. R-banding produces a pattern of bands that is the reverse of those in G-banded chromosomes. Banding technique G-banding — Treat metaphase spreads with trypsin, an enzyme that digests part of chromosomal protein. Stain with Giemsa stain. Observe banding pattern with light microscope. Q-banding — Treat metaphase spreads with the chemical quinacrine mustard. Observe fluorescent banding pattern with a special ultraviolet light microscope. R-banding — Heat metaphase spreads at high temperatures to achieve partial denaturation of DNA. Stain with Giemsa stain. Observe with light microscope. C-banding — Chemically treat metaphase spreads to extract DNA from the arms but not the centromeric regions of chromosomes. Stain with Giemsa stain and observe with light microscope. ©Csngags Learning. All Righls Reserved. Appearance of chromosomes 17 Darkly stained G bands. I> Bright fluorescent bands upon exposure to ultraviolet light; same as darkly stained G bands. 17 Darkly stained R bands correspond to light bands in G-banded chromosomes. Pattern is the reverse of G-banding. 4/ Darkly stained C band centromeric region of the chromosome corresponds to region of constitutive heterochromatin. gflflfl Picture Stats: Views: 347 Filesize: 411.48kB Height: 1500 Width: 1416 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=44292 |
