 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
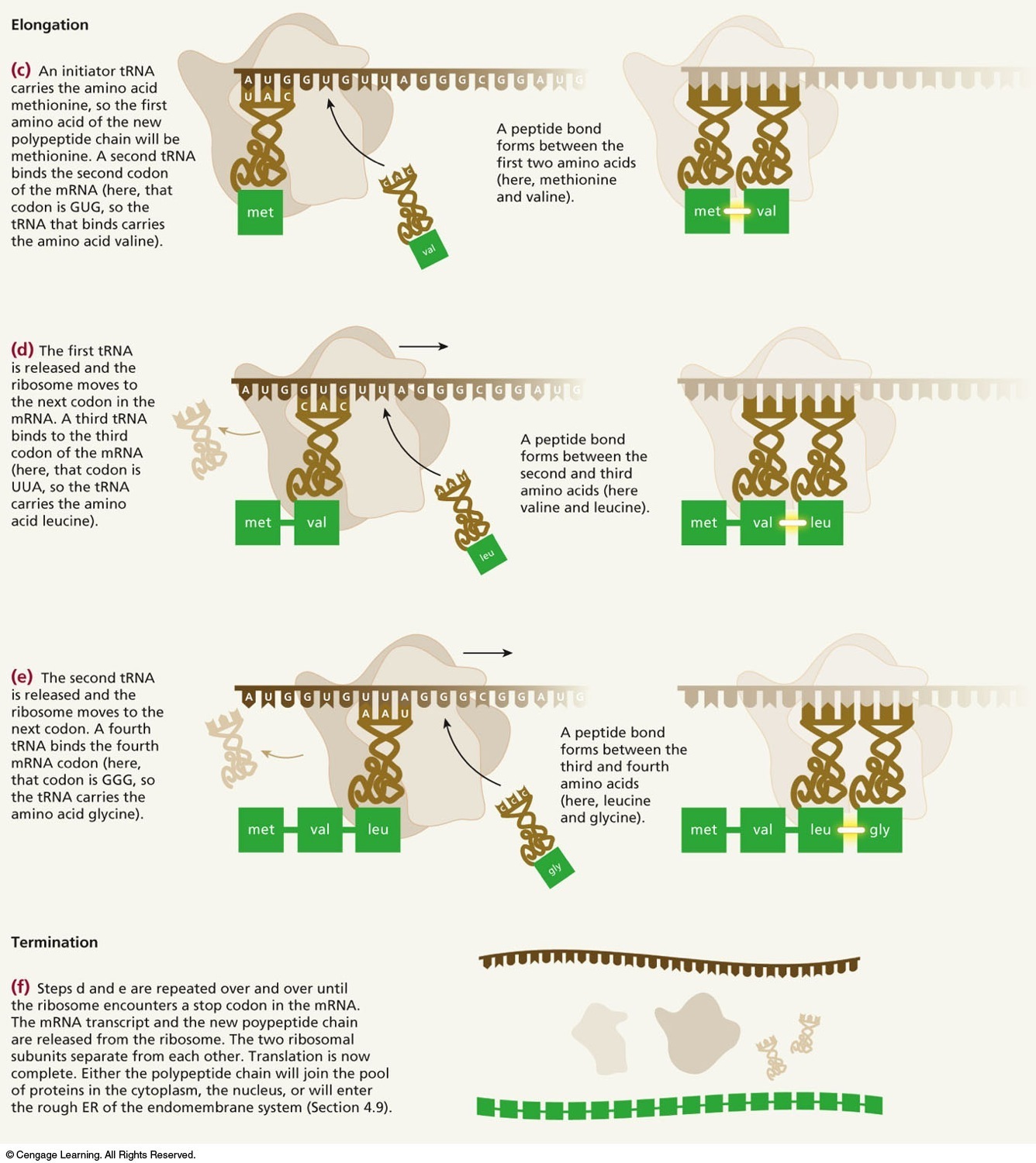
| Description: Elongation (c) An initiator tRNA carries the amino acid methionine, so the first amino acid of the new polypeptide chain will be methionine. A second tRNA binds the second codon of the mRNA (here, that codon is GUG, so the tRNA that binds carries the amino acid valine). A peptide bond forms between the first two amino acids (here, methionine and valine). (d) The first (RNA —> is released and the ribosome moves to the next radon in the mRNA. A third tRNA binds to the third \_/ A peptide bond codon of the mRNA forms between the (here, that codon is second and third UUA, so the tRNA amino acids (here carries the amino valine and leucine) acid leucine). val - leu (e) The second tRNA is released and the ribosome moves to the next codon. A fourth A peptide bond v V tRNA binds the fourth forms between the Q ‘ mRNA codon (here, third and fourth -‘ c -‘ . that codon is 666. so amino acids 4 , ’ the tRNA carries the (here, Ieucine \ . \ . amino acid glycine). and glycine)‘ leu —gh, Termination (0 Steps d and e are repeated over and over until the ribosome encounters a stop codon in the mRNA. The mRNA transcript and the new poypeptide chain are released from the ribosome. The two ribosomal subunits separate from each others Translation is now complete. Either the polypeptide chain will join the pool of proteins in the cytoplasm, the nucleus, or will enter the rough ER of the endomembrane system
Picture Stats: Views: 229 Filesize: 363.4kB Height: 1500 Width: 1336 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=44497 |
