 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
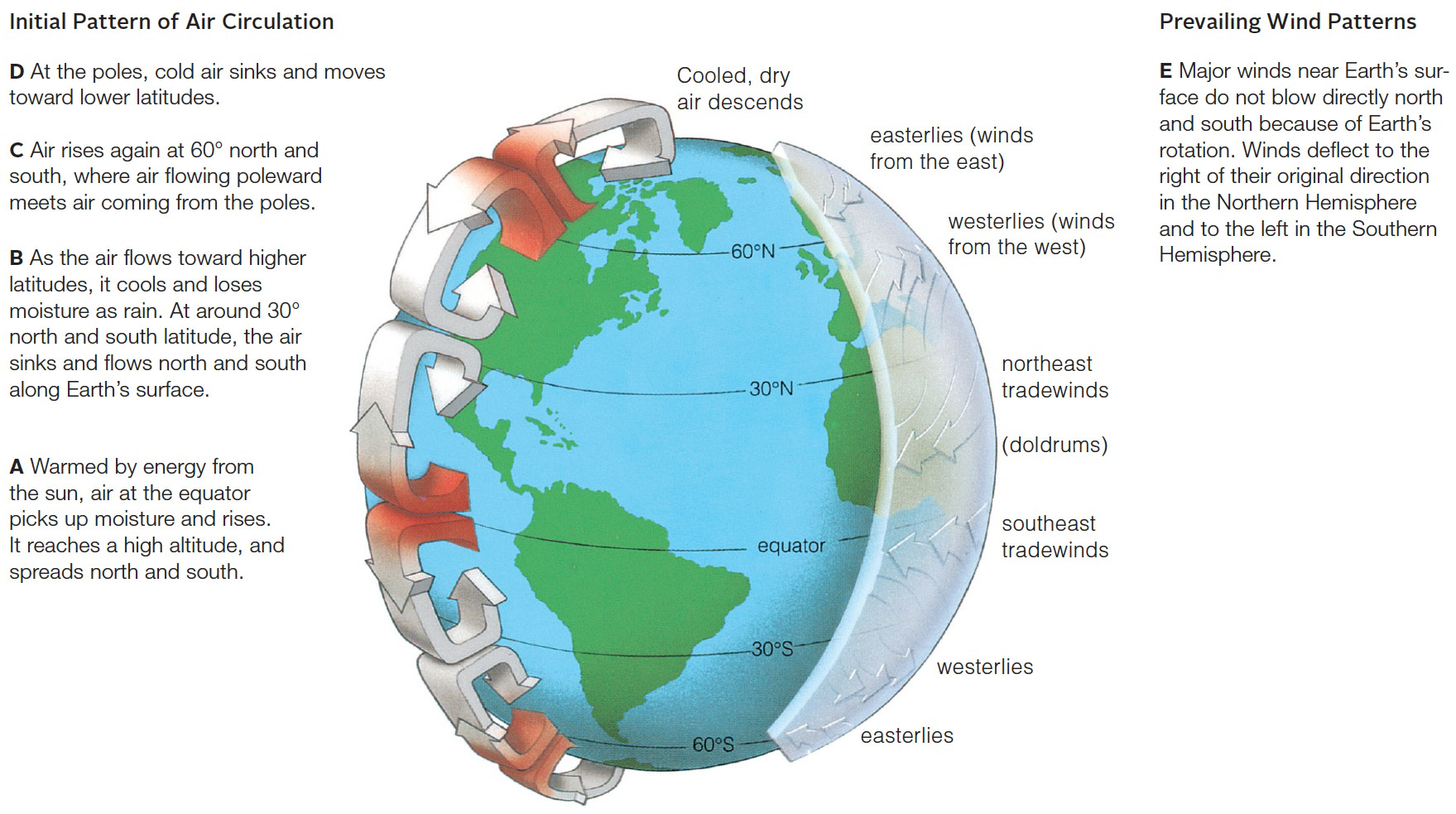
| Description: A Warmed by energy from the sun, air at the equator picks up moisture and rises. It reaches a high altitude, and spreads north and south. B As the air flows toward higher latitudes, it cools and loses moisture as rain. At around 30° north and south latitude, the air sinks and flows north and south along Earth’s surface. C Air rises again at 60° north and south, where air flowing poleward meets air coming from the poles. D At the poles, cold air sinks and moves toward lower latitudes. E Major winds near Earth’s sur-face do not blow directly north and south because of Earth’s rotation. Winds deflect to the right of their original direction in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. Initial Pattern of Air Circulation Prevailing Wind Patterns D At the poles, cold air sinks and moves Cooled, dry E Major winds near Earth’s sur- toward lower latitudes. air descends face do not blow directly north and south because of Earth’s rotation. Winds deflect to the right of their original direction in the Northern Hemisphere westerlies (winds and to the left in the Southern from the west) Hemisphere. easterlies (winds C Air rises again at 60 north and from the east) south, where air flowing poleward meets air coming from the poles. B As the air flows toward higher latitudes, it cools and loses moisture as rain. At around 30" north and south latitude, the air sinks and flows north and south along Earth’s surface. northeast tradewinds (doldrums) A Warmed by energy from the sun, air at the equator picks up moisture and rises. lt reaches a high altitude, and spreads north and south. southeast tradewinds Picture Stats: Views: 187 Filesize: 469.84kB Height: 983 Width: 1759 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=47269 |
