 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
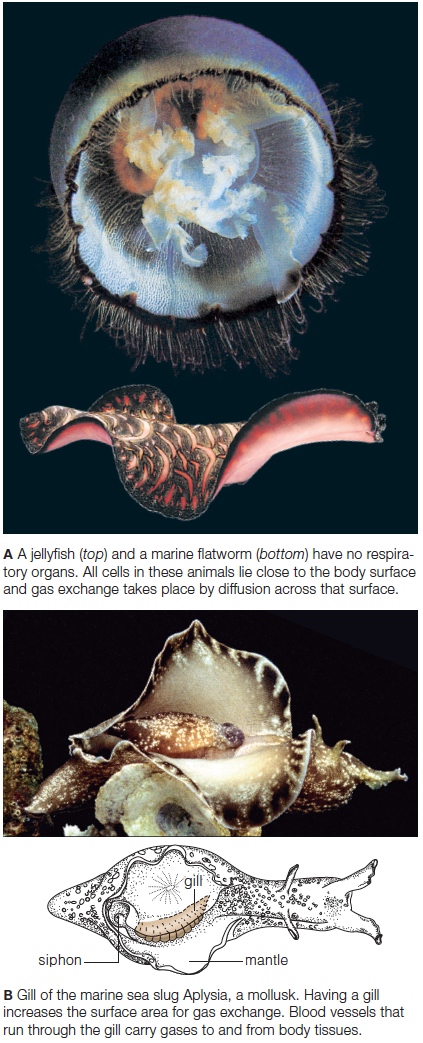
| Description: A. A jellyfish (top) and a marine flatworm (bottom) have no respiratory organs. All cells in these animals lie close to the body surface and gas exchange takes place by diffusion across that surface. B. Gill of the marine sea slug Aplysia, a mollusk. Having a gill increases the surface area for gas exchange. Blood vessels that run through the gill carry gases to and from body tissues Picture Stats: Views: 149 Filesize: 229.44kB Height: 1043 Width: 423 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=47470 |
