 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
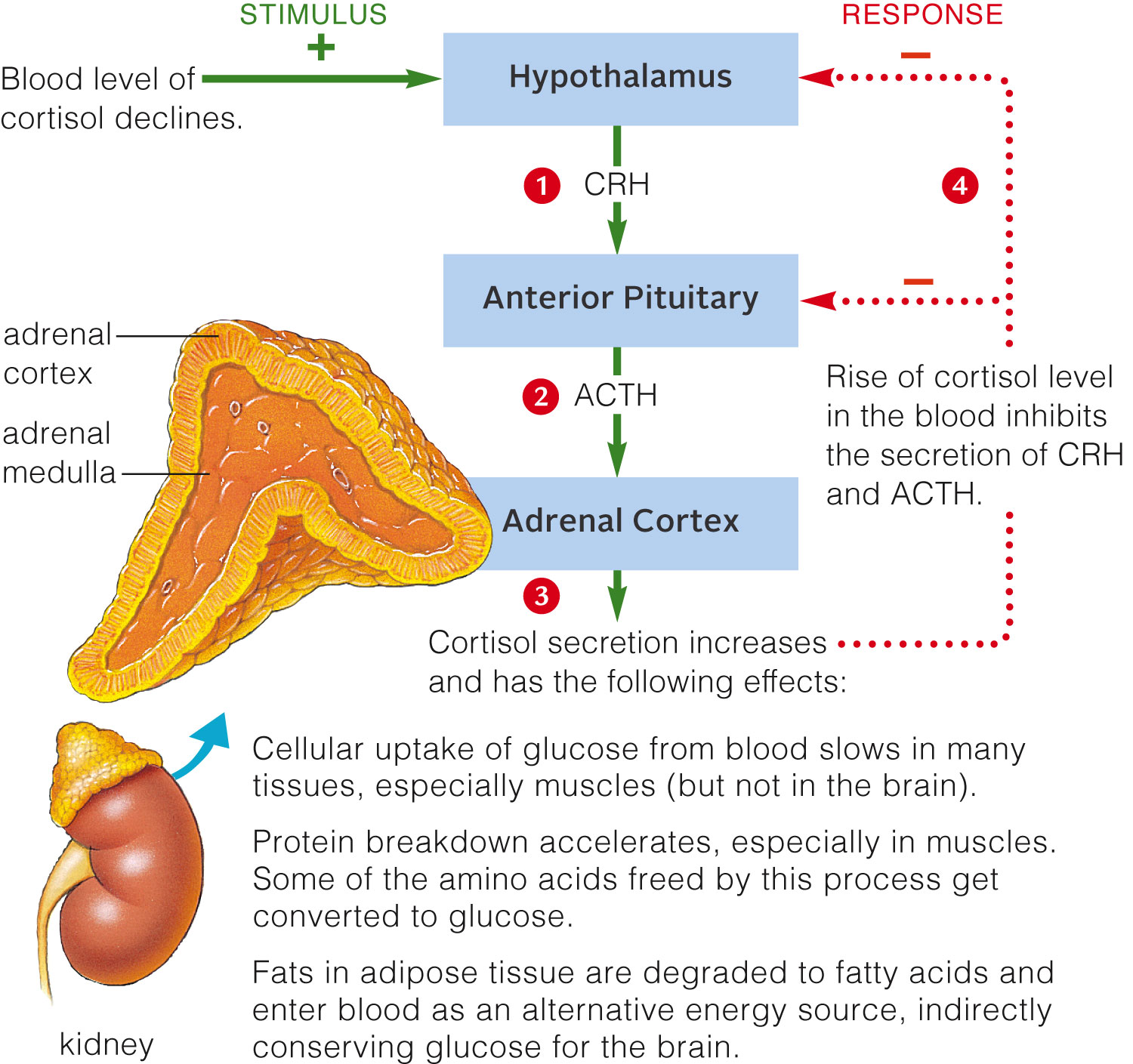
| Description: An adrenal gland rests on top of each kidney. The diagram shows a negative feedback loop that governs cortisol secretion. Cellular uptake of glucose from blood slows in many tissues, especially muscles (but not in the brain). Protein breakdown accelerates, especially in muscles. Some of the amino acids freed by this process get converted to glucose. Fats in adipose tissue are degraded to fatty acids and enter blood as an alternative energy source, indirectly adrenal cortex adrenal medulla kidney conserving glucose for the brain. An adrenal gland rests on top of each kidney. The diagram shows a negative feedback loop that governs cortisol secretion. Cellular uptake of glucose from blood slows in many tissues, especially muscles (but not in the brain). Protein breakdown accelerates, especially in muscles. Some of the amino acids freed by this process get converted to glucose. Fats in adipose tissue are degraded to fatty acids and enter blood as an alternative energy source, indirectly adrenal cortex adrenal medulla kidney conserving glucose for the brain. STIMULUS RESPONSE + _ Blood level of—> Hypothalamus 4........... cortisol declines. I o an l Anterior Pituitary 4-..7..." adrenal cortex 9 ACITH Rise of cortisol level adrenal in the blood inhibits medulla * the secretion of CRH and ACTH. Adrenal Cortex 9* Cortisol secretion increases and has the following effects: Cellular uptake of glucose from blood slows in many tissues, especially muscles (but not in the brain). Protein breakdown accelerates, especially in muscles. Some of the amino acids freed by this process get converted to glucose. Fats in adipose tissue are degraded to fatty acids and enter blood as an alternative energy source, indirectly kidney conserving glucose for the brain. Picture Stats: Views: 179 Filesize: 331.82kB Height: 1409 Width: 1500 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=47638 |
