 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
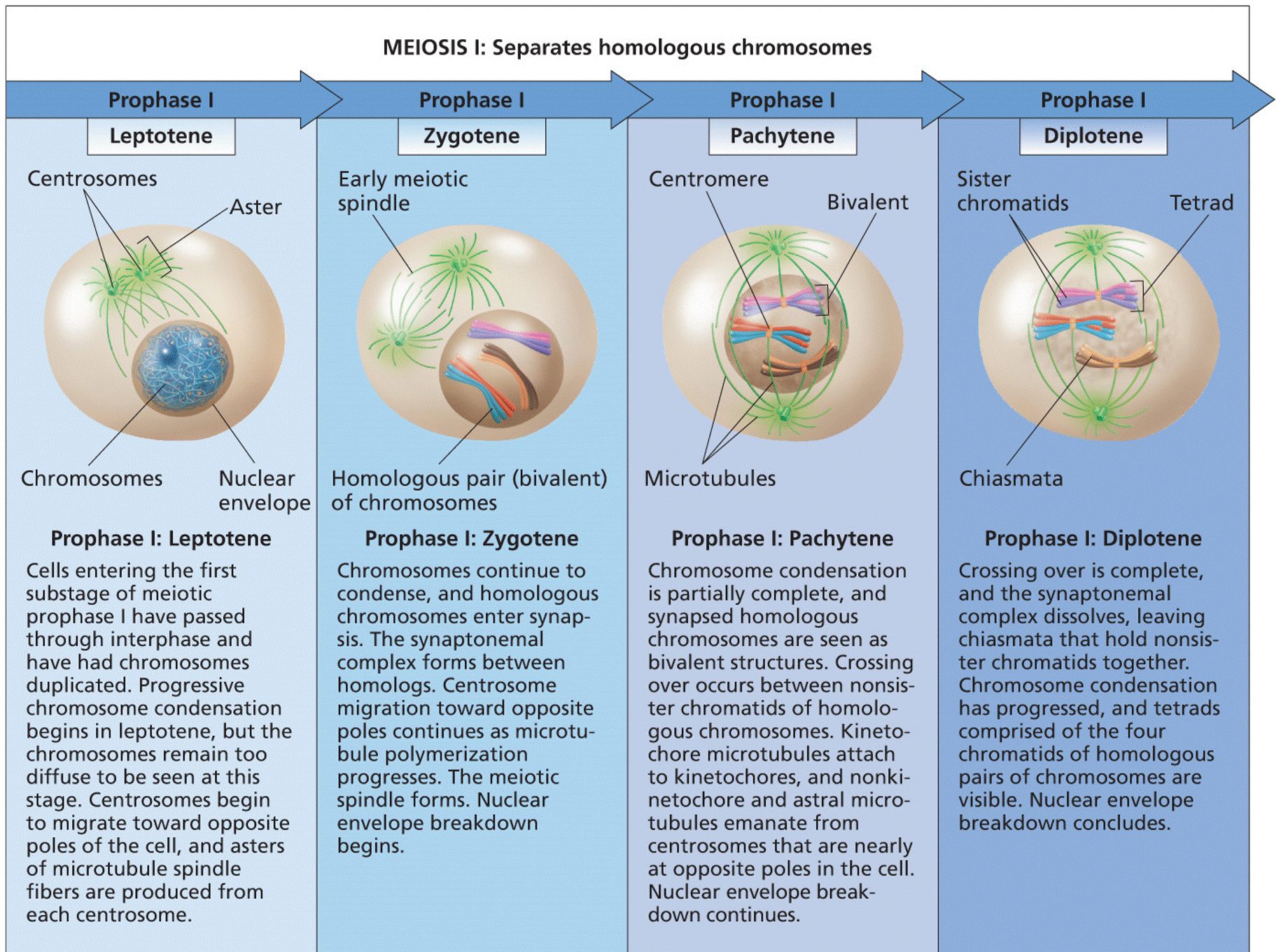
| Description: MEIOSIS I: Separates homologous chromosomes Prophase I Leptotene Centrosomes Nuclear envelope Chromosomes Prophase I: Leptotene Cells entering the first substage of meiotic prophase I have passed through interphase and have had chromosomes duplicated. Progressive chromosome condensation begins in leptotene, but the chromosomes remain too diffuse to be seen at this stage. Centrosomes begin to migrate toward opposite poles of the cell, and asters of microtubule spindle fibers are produced from each centrosome. Prophase I Zygotene Early meiotic spindle \. Homologous pair (bivalent) of chromosomes Prophase I: Zygotene Chromosomes continue to condense, and homologous chromosomes enter synap- sis. The synaptonemal complex forms between homologs. Centrosome migration toward opposite poles continues as microtu— bule polymerization progresses. The meiotic spindle forms. Nuclear envelope breakdown begins. Prophase I Centromere Bivalent Microtubules Prophase I: Pachytene Chromosome condensation is partially complete, and synapsed homologous chromosomes are seen as bivalent structures. Crossing over occurs between nonsis- ter chromatids of homolo- gous chromosomes. Kineto- chore microtubules attach to kinetochores, and nonki— netochore and astral micro- tubules emanate from centrosomes that are nearly at opposite poles in the cell. Nuclear envelope break- down continues. Prophase I Diplotene Sister chromatids Chiasmata Prophase I: Diplotene Crossing over is complete, and the synaptonemal complex dissolves, leaving chiasmata that hold nonsis- ter chromatids together. Chromosome condensation has progressed, and tetrads comprised of the four chromatids of homologous pairs of chromosomes are visible. Nuclear envelope breakdown concludes.
Picture Stats: Views: 85 Filesize: 1012.58kB Height: 1360 Width: 1830 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=48963 |
