 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
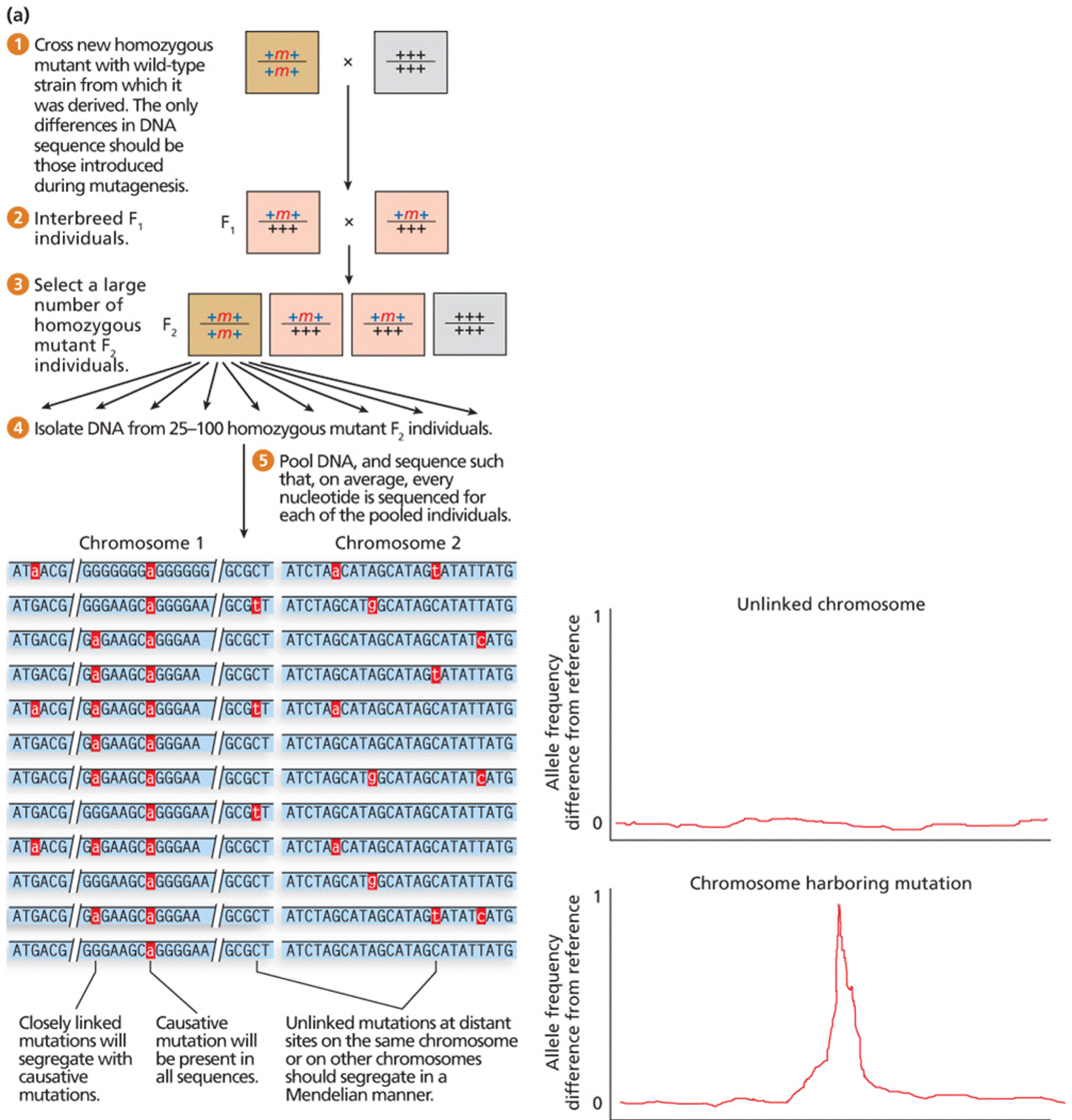
| Description: (a) Strategy to identify a mutant gene via genomic sequencing. (b) Example from Arabidopsis(a) Strategy to identify a mutant gene via genomic sequencing. (b) Example from Arabidopsis (a) 0 Cross new homozygous mutant with wild-type strain from which it was derived. The only differences in DNA sequence should be those introduced during mutagenesis. a Interbreed F, F individuals. homozygous mutant F oindiViduAais/A//\ N‘. elsolate DNA from 25-100 homozygous mutant F individuals. 9 Pool DNA. and sequence such that. on average, every nucleotide is uenced for each of the poo ed individuals. Chromosome 2 In 4......— x 9 Select a large number of Chromosome 1 Closely linked Causative Unlinked mutations at distant mutations will mutation will sites on the same chromosome segregate with be present in or on other chromosomes causative all sequences. should segregate in a mutations. Mendelian manner. Allele frequency difference from reference I Allele frequency difference from reference Unlinked chromosome _. Chromosome harboring mutation Picture Stats: Views: 245 Filesize: 387.2kB Height: 1513 Width: 1448 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=49331 |
