 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
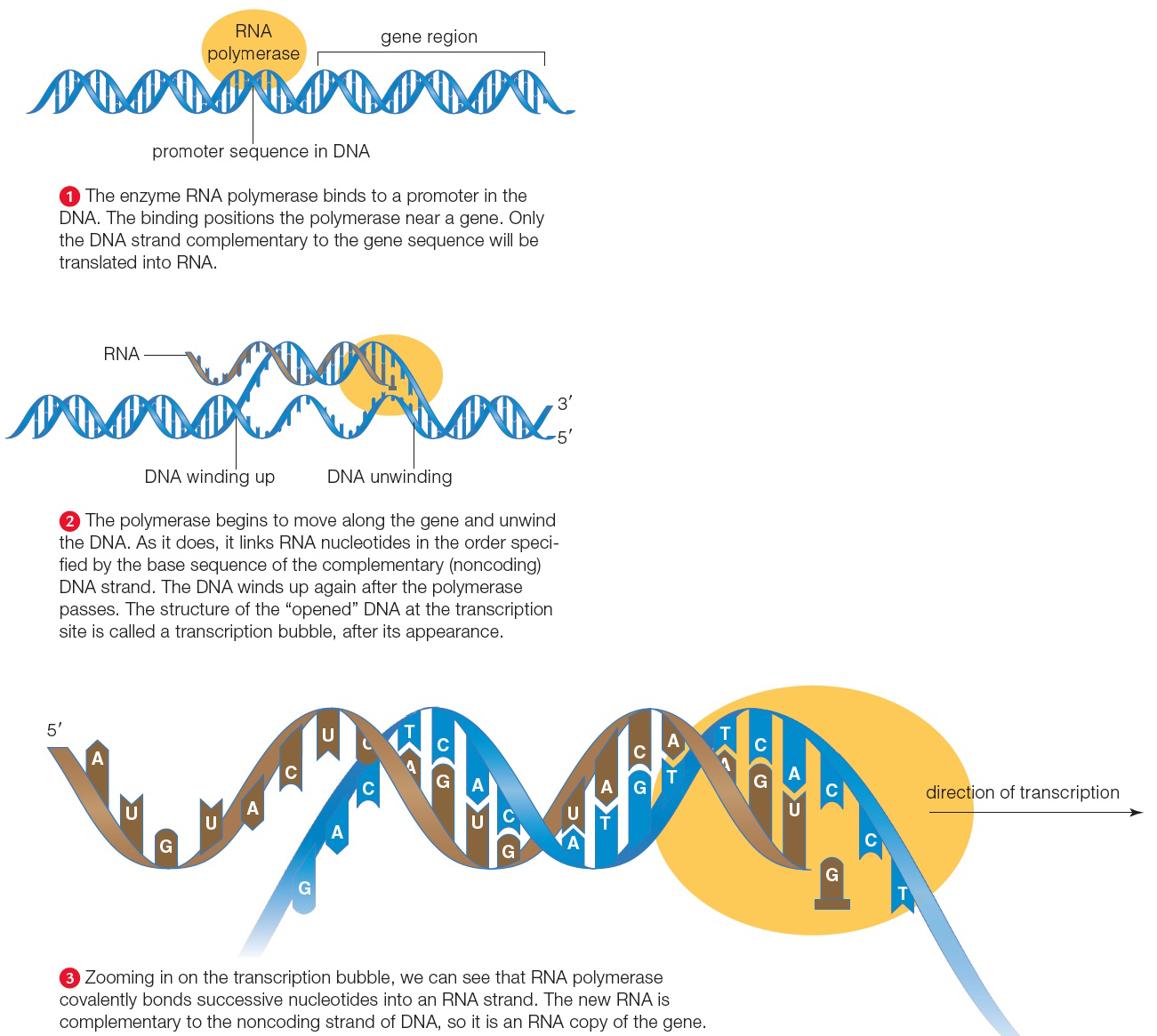
| Description: By this process, a strand of RNA is assembled from nucleotides according to a template: a gene region in DNA. Figure It Out: After the guanine, what is the next nucleotide that will be added to this growing strand of RNA? 1. RNA polymerase binds to a promoter in the DNA. The binding positions the polymerase near a gene. In most cases, the base sequence of the gene occurs on only one of the two DNA strands. Only the DNA strand complementary to the gene sequence will be translated into RNA. 2. The polymerase begins to move along the DNA and unwind it. As it does, it links RNA nucleotides into a strand of RNA in the order specified by the base sequence of the DNA. The DNA winds up again after the polymerase passes. The structure of the “opened” DNA at the transcription site is called a transcription bubble, after its appearance. 3. Zooming in on the gene region, we can see that RNA polymerase covalently bonds successive nucleotides into an RNA strand. The base sequence of the new RNA strand is complementary to the base sequence of its DNA template strand, so it is an RNA copy of the gene. Picture Stats: Views: 703 Filesize: 583.42kB Height: 1165 Width: 1301 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=49386 |
