 |
| Previous Image | Next Image |
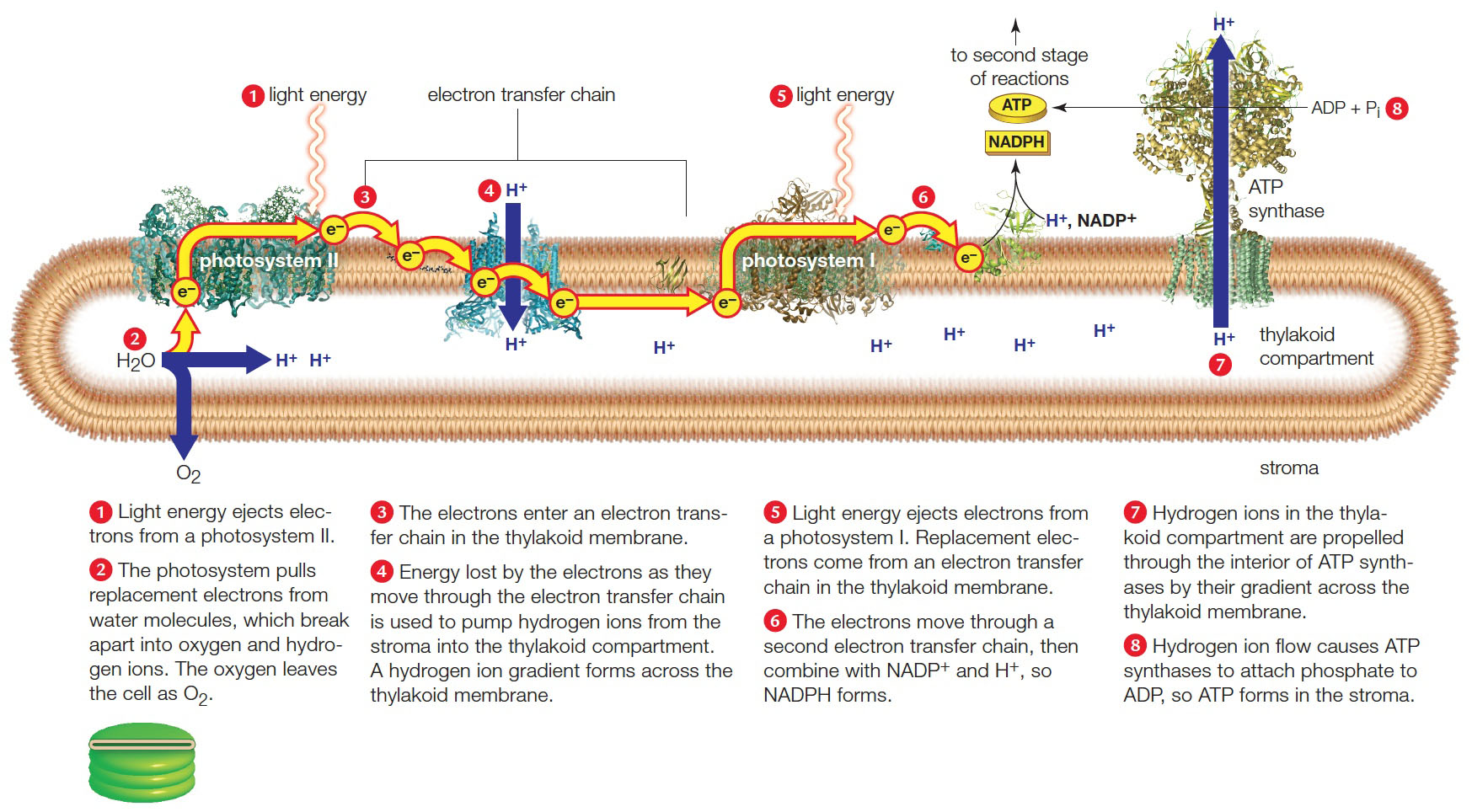
| Description: Noncyclic pathway of photosynthesis. Electrons that travel through two different electron transfer chains end up in NADPH, which delivers them to sugar-building reactions in the stroma. The cyclic pathway (not shown) uses a third type of electron transfer chain. 1 Light energy ejects electrons from a photosystem II. 2 The photosystem pulls replacement electrons from water molecules, which break apart into oxygen and hydro-gen ions. The oxygen leaves the cell as O2. 3 The electrons enter an electron transfer chain in the thylakoid membrane. 4 Energy lost by the electrons as they move through the electron transfer chain is used to pump hydrogen ions from the stroma into the thylakoid compartment. A hydrogen ion gradient forms across the thylakoid membrane. 5 Light energy ejects electrons from a photosystem I. Replacement elec-trons come from an electron transfer chain in the thylakoid membrane. 6 The electrons move through a second electron transfer chain, then combine with NADP+ and H+, so NADPH forms. 7 Hydrogen ions in the thylakoid compartment are propelled through the interior of ATP synthases by their gradient across the thylakoid membrane. 8 Hydrogen ion flow causes ATP synthases to attach phosphate to ADP, so ATP forms in the stroma. Picture Stats: Views: 766 Filesize: 366.06kB Height: 964 Width: 1747 Source: https://biology-forums.com/index.php?action=gallery;sa=view;id=49477 Keywords: Photosynthesis |
